Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which structure-function pair is incorrectly matched?
Vacuole — Digestion, waste disposal, and storage | |
Chloroplast — Photosynthesis | |
Ribosome — Synthesis of lipids, detoxification of drugs and poisons | |
Lysosome — Breakdown of ingested substances, damaged organelles recycled |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Ribosomes are responsible for polypeptide synthesis and are located both free in the cytoplasm and on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes lipids and detoxifies drugs and poisons.
Question 2 |
Which of the following statements regarding the nucleus is false?
Cellular Respiration | |
Houses chromosomes | |
Contains chromatin | |
Surrounded by a double membrane |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration.
Question 3 |
Which part of the cell allows the cell to discriminate in its chemical exchanges with its environment?
Cytoskeleton | |
Cilia | |
Plasma Membrane | |
Cell Wall |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The plasma membrane controls molecular traffic into and out of the cell. It is selectively permeable, meaning it allows some substances to enter the cell, but not others. This is essential because it call keep many harmful or dangerous substances from entering and destroying the cell while still allowing the necessary substances to enter.
Question 4 |
Which statement is true of both mitochondria and chloroplasts?
Both play a role in energy conversion | |
Both are sites of cellular respiration | |
Both convert energy from sugar, fats and other fuels into ATP | |
They are both part of the endomembrane system |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Mitochondria generate ATP by extracting energy from sugars, fats and other fuels to make energy available in animal cells. Chloroplasts convert solar energy into chemical energy to make sugar available for plant cells. Thus, they both convert energy into a form that the cell can use.
Question 5 |
Which of the following is not part of the endomembrane system?
Endoplasmic reticulum | |
Golgi apparatus | |
Lysosomes | |
Mitochondria |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). All other choices are part of the endomembrane system. The mitochondria are the site of cellular respiration.
Question 6 |
Which group of organelles works together to regulate protein traffic and performs metabolic functions of the cell?
Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, and vacuoles | |
Nucleus and ribosomes | |
Mitochondria, chloroplast, peroxisome | |
Nuclear envelope, nucleolus, chromatin |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The eukaryotic cell’s genetic functions are housed in the nucleus and carried out by the ribosomes. The mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another. The nuclear envelope, nucleolus and chromatin are all part of the nucleus.
Question 7 |
Although animal cells lack cell walls, they have a complex network of glycoproteins that provide structure and strength to the cell, referred to as:
Desmosomes | |
Extracellular matrix | |
Intermediate filaments | |
Cytoskeleton |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Desmosomes are intercellular junctions that function like rivets. Intermediate filaments are a group of cytoskeletal elements. The cytoskeleton refers to the fibers that organize activities and structures inside the cell.
Question 8 |
Which group of cellular structures form the endomembrane system?
Microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments | |
Endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles | |
Mitochondria and chloroplasts | |
Fimbriae, nucleoid, flagella |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments are parts of the cytoskeleton structure. The endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles form the endomembrane system. The mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another. Fimbriae, nucleoid and flagella are components of a prokaryotic cell.
Question 9 |
White blood cells engulf invading bacterium in a process called:
Phagocytosis | |
Pinocytosis | |
Receptor-mediated endocytosis | |
Exocytosis |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Phagocytosis is the process by which cells engulf a particle by wrapping pseudopodia around it and packaging it into vacuoles.
Question 10 |
Which description best matches the diagram?
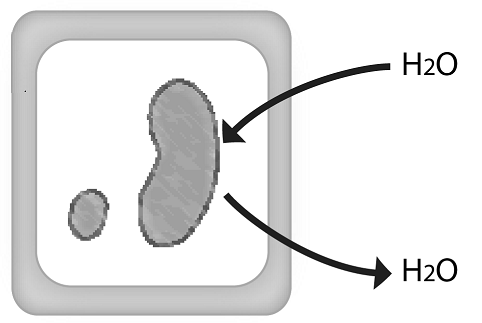
An animal cell in a hypertonic solution | |
An animal cell in a hypotonic solution | |
A plant cell in an isotonic solution | |
A plant cell in a hypotonic solution |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The diagram is showing a plant cell (notice the cell walls). If a cell is immersed in an isotonic solution, there will be no net movement of water. In other words, water will move in and out of the cell at an equal rate.
Question 11 |
Which diagram below shows the correct order diffusion of solute in water across a membrane?
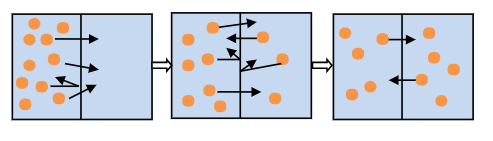 | |
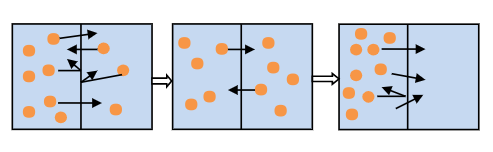 | |
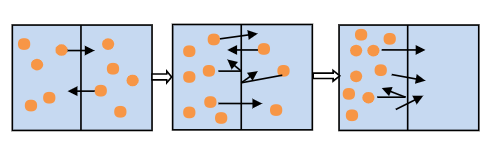 | |
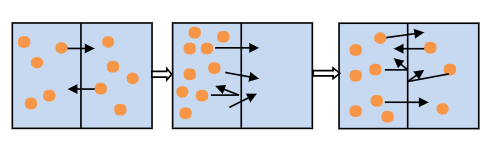 |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). There is a net movement of solutes across membranes from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until they reach equilibrium.
Question 12 |
Which answer correctly describes what is happening in the following diagram?
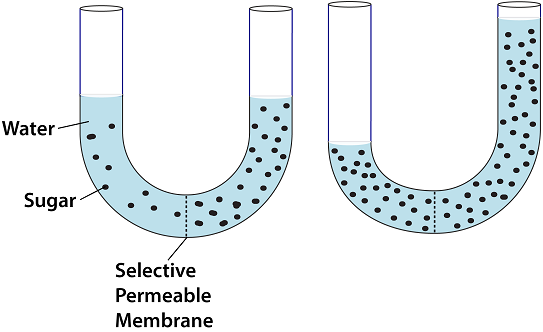
Diffusion of sugar from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration | |
Osmosis of water from an area of low water concentration to an area of high water concentration | |
Osmosis of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high concentration | |
Osmosis of sugar from an area of low water concentration to an area of high water concentration |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The sugar molecules are too large to move across the selectively permeable membrane. The water molecules move from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to the area of low water concentration (high solute concentration) until the solution reaches equilibrium.
Question 13 |
In the diagram below, what is the arrow pointing to?
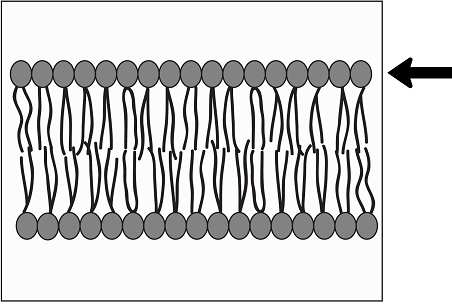
Hydrophilic portion of the phospholipid bilayer | |
Hydrophobic portion of the phospholipid bilayer | |
Transport proteins | |
The extracellular matrix |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The plasma membrane’s phospholipid bilayer is made up of two layers of phospholipids. Phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water loving) head and a hydrophoboic (water hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads are attracted to water, and therefore make up the outer part of the phospholipid bilayer.
Question 14 |
Which of the following statements is not true of a plasma membrane protein:
May aid in the transport of materials from one side of the membrane to the other | |
Membrane proteins of adjacent cells may hook together in various kinds of junctions | |
May be an enzyme or series of enzymes involved in metabolic pathways | |
May be a membrane carbohydrate used for cell-to-cell recognition |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Membrane proteins are made of protein, Answer (D) describes a carbohydrate.
Question 15 |
Which of the following is an example of active transport used by the cell to maintain internal concentrations of small solutes different form concentrations in the environment?
Facilitated diffusion | |
Osmoregulation | |
Sodium-potassium pump | |
Bulk transport |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The sodium-potassium pump exchanges sodium for potassium across the plasma membrane of animal cells by pumping ions against steep concentration gradients.
Question 16 |
How do large particles, such as proteins and polysaccharides, generally cross the plasma membrane into cells?
Exocytosis | |
Endocytosis | |
Cotransport | |
Gated channels |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Endocytosis is the process by which a cell takes in substances by engulfing them in new vesicles formed from the plasma membrane.
Question 17 |
What cellular structure is responsible for its selective permeability?
Plasma membrane | |
Cytoplasm | |
Nucleus | |
Cytoskeleton |
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The phosolipid bilayer of the plasma membrane allows some molecules to enter while keeping other molecules out.
Question 18 |
The pumping of substances across a membrane against the direction of spontaneous movement is which type of work?
Diffusion | |
Active Transport | |
Dialysis | |
Filtration |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Active transport involves the use of transport proteins to move solutes against a concentration gradient, which means they are pumping something (typically ions) from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.
Question 19 |
Which of the following is not a type of intracellular junction in animal cells?
Desmosomes | |
Gap Junctions | |
Tight Junctions | |
Plasmodesmata |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Plasmodesmata are channels in cell walls of plant cells.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 19 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Cellular Energetics >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
