Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which is the correct sequence of information flow in a cell?
DNA → RNA → Protein | |
Protein → DNA → RNA | |
DNA → Protein → RNA | |
RNA → DNA → Protein |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Each gene on a DNA molecule directs the synthesis of a messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA molecule directs the production of a polypeptide.
Question 2 |
Which is the correct sequence of mitosis?
Metaphase → Prophase → Anaphase → Telophase → Prometaphase | |
Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase | |
Prometaphase → Metaphase → Prophase → Anaphase → Telophase | |
Telophase → Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The cell cycle progresses through phases of the cell cycle in the following order:
Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase
Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase
Question 3 |
If a cell has 6 chromosomes in metaphase, how many chromatids would it have?
6 | |
3 | |
12 | |
None |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Each duplicated chromosome has two sister chromatids. Therefore, 6 chromosomes would include 12 chromatids.
Question 4 |
If a zygote went through a series of 4 cell divisions, how many cells would be in the embryo?
32 | |
10 | |
16 | |
8 |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Each time a cell divides, it become two cells. To calculate the number of cells, square the number of cell divisions; 42 = 16.
Question 5 |
Questions 5–8
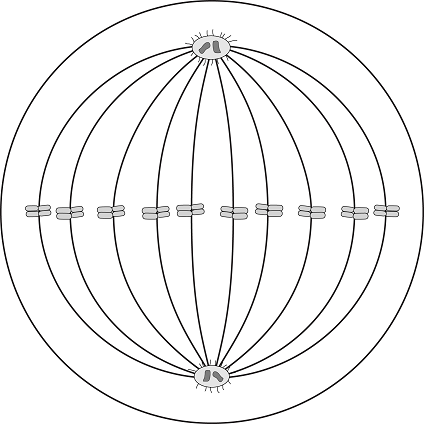
What phase of the cell cycle is represented by the diagram?
Metaphase | |
Prophase | |
Interphase | |
Cytokinesis |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). During metaphase, the chromosomes are lined up along the metaphase plate, the centrosomes are at opposite poles, the kinetochores of the sister chromatids are attached to microtubules coming from opposite poles.
Question 6 |
Questions 5–8

Swamp wallabies have 10 chromosomes during this phase. How many chromosomes did the wallaby inherit from each parent?
10 | |
5 | |
20 | |
15 |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Somatic cells, like the one pictured here in metaphase, are diploid. If the diploid number is 10, then the organism inherited 5 chromosomes from each parent (the haploid number).
Question 7 |
Questions 5–8

How many chromosomes are in each of the wallabies' gametes?
10 | |
5 | |
20 | |
15 |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Sex cells (gametes) have half the number of chromosomes as somatic cells.
Question 8 |
Questions 5–8

How many chromosomes will be in each of the wallaby’s offspring?
10 | |
5 | |
20 | |
15 |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Offspring have the same number of chromosomes as their parents.
Question 9 |
Which types of organisms have a sexual life cycle known as the alternation of generations?
Animals | |
Plants and fungi | |
Bacteria | |
Archaea |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Alternation of generations is a type of life cycle in which both diploid and haploid stages are multicellular. The sporophyte generation produces a gametophyte as its offspring and the gametophyte generation produces the next sporophyte generation.
Question 10 |
Which of the following is not a difference between the cell cycle and meiosis?
The cell cycle produces cells for growth and repair. Meiosis produces gametes. | |
Cells divide one time in the cell cycle. Cells divide two times in meiosis. | |
The cell cycle produces cells genetically identical to the parent cell. Meiosis produces cells genetically different from the parent and from each other. | |
In the cell cycle, crossing over takes place during metaphase. In meiosis, crossing over takes place during prophase I. |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Crossing over only takes place during meiosis.
Question 11 |
Which of the following does not produce genetic variation in sexual life cycles?
Crossing over | |
Binary fission | |
Independent assortment of chromosomes | |
Random fertilization |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Binary fission is the type of asexual reproduction used by single-celled eukaryotes, such as amoebas, and prokaryotes.
Question 12 |
Questions 12–13
Pea plants heterozygous for pod shape and pod color were allowed to self pollinate, and 400 resulting seeds were planted. How many offspring would be predicted to have constricted and yellow?
16 | |
25 | |
75 | |
225 |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). First define the variables and then create a chart:
Inflated Pod Shape = I
Constricted Pod Shape = i
Green Pod Color = G
Yellow Pod Color = g
Cross: IiGg x IiGg
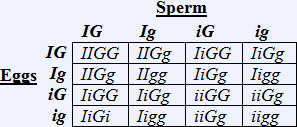
Inflated and Green: 9/16
Inflated and Yellow: 3/16
Constricted and Green: 3/16
Constricted and Yellow: 1/16
1/16 of 400 = 25
Inflated Pod Shape = I
Constricted Pod Shape = i
Green Pod Color = G
Yellow Pod Color = g
Cross: IiGg x IiGg

Inflated and Green: 9/16
Inflated and Yellow: 3/16
Constricted and Green: 3/16
Constricted and Yellow: 1/16
1/16 of 400 = 25
Question 13 |
Questions 12–13

How many different gametes could be made from a pea plant heterozygous for flower color, flower position and stem length?
27 | |
6 | |
8 | |
64 |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C).
Purple Flower Color = P
White Flower Color = p
Axial Flower Position = A
Terminal Flower Position = a
Tall Stem Length = T
Dwarf Stem Length = t
Gametes are as follows: PAT, PAt, PaT, Pat, pAT, pAt, paT, pat
Purple Flower Color = P
White Flower Color = p
Axial Flower Position = A
Terminal Flower Position = a
Tall Stem Length = T
Dwarf Stem Length = t
Gametes are as follows: PAT, PAt, PaT, Pat, pAT, pAt, paT, pat
Question 14 |
Which of the following is not a component of DNA?
Sugar | |
Phosphate | |
Nucleotide | |
Uracil |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Uracil is a RNA nucleotide.
Question 15 |
What aspect of the DNA molecule allows for it to replicate a duplicate copy of itself?
Base Pairing | |
Double helix structure | |
Origins of replication | |
Looped Domains |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The two strands of DNA are complimentary, which allows one strand to serve as a template for ordering nucleotides into a new, complimentary strand.
Question 16 |
What is the name of the DNA strand that elongates away from the replication fork in a series of segments?
Okazaki fragments | |
Lagging strand | |
Leading strand | |
Primer |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Since DNA is elongated in the 5' → 3' direction, only one strand can be elongated continuously. On the other strand, it must be replicated in segments since it can only be replicated in the 5' → 3', and this strand goes from 3' → 5'.
Question 17 |
DNA replication begins at short stretches of DNA with a specific sequence of nucleotides called:
Origins of replication | |
Template sequence | |
Replication fork | |
Replication bubble
|
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Origins of replication contain specific sequences of nucleotides where DNA replication begins.
Question 18 |
Which enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA by adding nucleotides to a preexisting chain?
DNA ligase | |
DNA polymerase | |
Helicase | |
Topoisomerase |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). DNA polymerase is responsible for adding nucleotides to a preexisting chain. DNA ligase joins together sugar-phosphate backbones of the Okazaki fragments into a continuous strand of DNA. Helicase unwinds parental double helix at replication forks. Topoisomerase breaks, swivels and rejoins DNA strands ahead of replication forks to relieve overwinding strain ahead of the replication forks.
Question 19 |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy affects 1 in 3,500 males born in the United States. This disease is characterized by the progressive loss of coordination and weakening of the muscles, and those with Dushcenne muscular dystrophy have a shorter than average lifespan. This disorder was traced to the absence of a muscle protein called dystrophin, for which the gene is located on X chromosome.
This gene is an example of:
An X inactivation | |
A barr body | |
A sex-linked gene | |
Recombination |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Sex-linked genes are any genes located on a sex chromosome. In humans, such genes are often found on the X chromosome.
Question 20 |
Chromosome structure can be altered by damages to the chromosome, or during an error in meiosis.
When a chromosomal fragment reattaches to the original chromosome in reverse order, it is called:An inversion | |
A translocation | |
A deletion | |
A duplication |
Question 20 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). A deletion occurs when a chromosome fragment is lost. A duplication leads to the addition of one or copies of a preexisting DNA sequence to a chromosome. A translocation is the result of a chromosomal breakage during which the fragment of one chromosome joins a nonhomologous chromosome resulting in a rearrangement of DNA.
Question 21 |
The ABO blood groups in humans are determined by the following alleles of a single gene: IA, IB, and i. The four blood types, A, B, AB and O are determined by which genes are inherited from the parents. This pattern of inheritance pattern is called:
Pleiotropy | |
Epistasis | |
Multiple alleles | |
Codominance |
Question 21 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Multiple alleles exist when more than two alleles exist for a gene.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 21 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Expression of Genetic Information >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
