Our AP World History Unit 7 practice test covers global conflict. This section of the curriculum goes from the year 1900 to the present and introduces topics such as: the global political order and mass atrocities post-1900, World War I, the interwar period, and World War II. Start your Unit 7 test prep with these free multiple choice practice questions.
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Questions 1–5 refer to the passage below.
What General Weygand has called The Battle of France is over. The battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilisation. Upon it depends our own British life and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of a perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, “This was their finest hour.”
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
What does Winston Churchill's reference to "The Battle of France is over. The battle of Britain is about to begin" signify in the context of World War II?
The end of military operations in Europe | |
A shift in the focus of Nazi Germany's military campaign from France to Britain | |
The conclusion of World War II | |
The beginning of peace negotiations between Britain and Germany |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Churchill's statement marks the transition from the successful German campaign in France, culminating in France's defeat, to the impending military efforts aimed at Britain. This signifies a critical phase in World War II where Britain became the primary target of Nazi aggression in the West.
Question 2 |
What General Weygand has called The Battle of France is over. The battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilisation. Upon it depends our own British life and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of a perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, “This was their finest hour.”
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
According to Churchill, what was at stake in the Battle of Britain?
The territorial integrity of the British Empire alone | |
Economic dominance in Europe | |
The survival of Christian civilization and the future of democratic institutions | |
A temporary shift in military alliances |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Churchill emphasizes the existential threat posed by Nazi Germany, framing the Battle of Britain as a pivotal moment not only for the UK but for the preservation of Christian civilization and democratic values worldwide. He suggests that the outcome would determine the future direction of global affairs, potentially leading to a new Dark Age if Britain were to fail.
Question 3 |
What General Weygand has called The Battle of France is over. The battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilisation. Upon it depends our own British life and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of a perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, “This was their finest hour.”
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
What does Churchill imply about the role of the United States in his speech?
That the United States was already actively involved in the conflict | |
That the fate of the United States was intertwined with the outcome of the Battle of Britain | |
That the United States was indifferent to the outcome of the war | |
That the United States would lead the charge against Nazi Germany |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Churchill's inclusion of the United States in his speech underscores the global implications of the battle, suggesting that even countries not yet directly involved in the conflict, like the US, would be affected by its outcome. He highlights the interconnectedness of the democratic world and the universal threat posed by Nazi Germany.
Question 4 |
What General Weygand has called The Battle of France is over. The battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilisation. Upon it depends our own British life and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of a perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, “This was their finest hour.”
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
How does Churchill's speech use the differing imagery of "broad, sunlit uplands" and "the abyss of a new Dark Age"?
To contrast the potential outcomes of victory versus defeat | |
As a metaphor for the changing seasons in Britain | |
To describe the geographical advantages of Britain | |
To highlight the technological advancements of the time |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Churchill employs the imagery of "broad, sunlit uplands" to evoke a vision of a hopeful, liberated future that victory could secure, in stark contrast to the "abyss of a new Dark Age" that defeat might bring. This rhetorical device serves to underscore the existential stakes of the Battle of Britain, motivating his audience by illustrating the dire consequences of failure versus the bright prospects of success.
Question 5 |
What General Weygand has called The Battle of France is over. The battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilisation. Upon it depends our own British life and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of a perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, “This was their finest hour.”
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
—Winston Churchill, This Was Their Finest Hour, 1940
What is implied by Churchill's statement, "if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, 'This was their finest hour'"?
That the British Empire was on the verge of collapse | |
That the resolve and bravery shown during the Battle of Britain would be remembered as a defining moment of courage and unity | |
That future conflicts would overshadow the events of World War II | |
That the significance of the Battle of Britain was overstated |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Churchill's statement encapsulates the enduring legacy he envisioned for the Battle of Britain within the annals of British history. He suggests that the courage, determination, and unity displayed by Britain in the face of Nazi aggression would be celebrated as a pinnacle of national character and resolve, regardless of the Empire's future.
Question 6 |
Questions 6–10 refer to the map below.
Territories of the British Empire in 1897 are shown in red.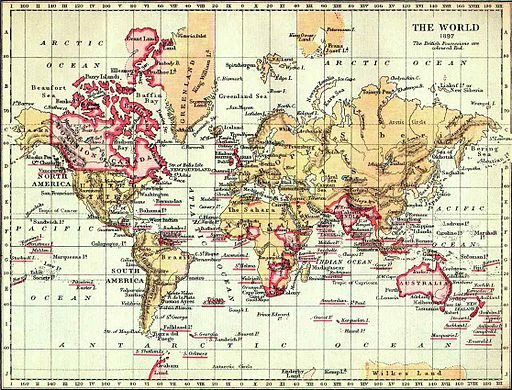
What does the red coloring on the map of the British Empire in 1897 demonstrate about Britain's global influence at the time?
Its limited reach to only a few strategic locations | |
The dominance of British naval power | |
The vast territorial extent of the British Empire across multiple continents | |
The economic independence of its colonies |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The map, with extensive areas colored in red to denote British possessions, visually represents the phrase "the sun never sets on the British Empire." This expression highlights the global span of the empire, indicating that at any given time of the day, the sun was shining on at least one of its territories. This vast territorial control underscores Britain's significant global influence, both politically and economically, during the late 19th century.
Question 7 |
Territories of the British Empire in 1897 are shown in red.


How did the distribution of British possessions in 1897 contribute to the empire's economic system?
It provided a diverse range of climates for agriculture | |
It facilitated control over key trade routes and resources | |
It encouraged the development of local industries in colonies | |
It limited Britain's involvement in international trade |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The strategic locations of British possessions allowed the empire to control crucial trade routes and access valuable resources, such as spices, tea, cotton, and gold. This control not only bolstered Britain's economic dominance but also integrated the colonies into a global trade network centered around British interests, contributing significantly to the wealth of the empire.
Question 8 |
Territories of the British Empire in 1897 are shown in red.


What role did the British Empire's territorial acquisitions play in the geopolitical landscape of the late 19th century?
They led to increased isolationism within Britain | |
They contributed to rivalries and tensions with other imperial powers | |
They decreased Britain's interest in European affairs | |
They encouraged a global movement toward decolonization |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The expansion of the British Empire and its control over vast territories and resources were a source of envy and competition among other European powers, such as France, Germany, and the Netherlands. This scramble for colonies often led to diplomatic tensions and conflicts, shaping the geopolitical landscape of the era and setting the stage for alliances and rivalries that would later influence global events like World War I.
Question 9 |
Territories of the British Empire in 1897 are shown in red.


In what way did the British Empire's global presence in 1897 impact cultural exchanges and the spread of ideas?
It facilitated the movement of people, goods, and ideas across its territories | |
It promoted the uniform adoption of British culture in all colonies | |
It discouraged interactions between different cultural groups | |
It limited the influence of non-British ideas within the empire |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The British Empire acted as a conduit for cultural exchanges, spreading British ideas, languages, and customs around the world while also bringing diverse cultures into contact with each other. This exchange influenced language, education, legal systems, and social customs in the colonies, leaving a lasting impact on the cultural landscapes of many countries.
Question 10 |
Territories of the British Empire in 1897 are shown in red.


What strategic advantage did the British Empire's global distribution of territories offer in terms of military and defense capabilities?
It enhanced the ability to project power and defend interests worldwide | |
It limited the capacity for defense due to overextension | |
It led to a focus on continental Europe at the expense of overseas territories | |
It created dependence on local militias with little central control |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The global distribution of British territories provided strategic naval bases and ports, allowing Britain to project military power across the world's oceans and defend its commercial and colonial interests against rivals. This network of bases enabled rapid deployment of the Royal Navy, contributing to Britain's status as the world's preeminent naval power at the time.
Question 11 |
Questions 11–15 refer to the political cartoon below.

The political cartoon "Turkey Limited" from Punch in 1896 is best understood in the context of which statement?
The Ottoman Sultan was taken down by a military leader | |
The Ottoman Empire was in a state of decline prior to World War I | |
The Ottoman Sultan has absolute religious and political authority over citizens | |
The Ottoman Empire initially fought World War I with the Central Powers |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The cartoon reflects the European perspective on the "Sick Man of Europe," a term used to describe the Ottoman Empire due to its gradual weakening and loss of territories to European powers throughout the 19th century. This decline was recognized by Russia, France, and England, who were keenly interested in the strategic military and economic value of Ottoman territories as the empire weakened.
Question 12 |

Which statement best explains the collapse of the Ottoman Empire?
The internal reforms known as the Tanzimat | |
The annexation of Bosnia by Austria-Hungary | |
The rise of Jingoism as a foreign policy strategy | |
The inability to pay debts following the Crimean War |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). While the Tanzimat reforms aimed at modernization and the annexation of Bosnia by Austria-Hungary were significant events, the empire's financial ruin following the Crimean War critically undermined its stability. The massive debts incurred led to economic vulnerability, which, coupled with internal strife and nationalist movements within its territories, precipitated the empire's decline and eventual collapse.
Question 13 |

How does the cartoon "Turkey Limited" illustrate the European powers' view of the Ottoman Empire's geopolitical situation in the late 19th century?
It highlights the empire's military prowess | |
It depicts the empire as a diminishing power in need of partitioning among European nations | |
It showcases the empire's economic prosperity | |
It emphasizes the sultan's control over global politics |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The cartoon portrays the Ottoman Empire as weak and vulnerable, subject to the interests and interventions of European powers. This reflects the period's "Great Game," where European nations, including Russia, France, and England, were vying for influence and territory in regions formerly under Ottoman control, viewing the empire's decline as an opportunity to expand their own empires.
Question 14 |

What impact did the financial instability following the Crimean War have on the Ottoman Empire's internal and external relations?
It led to increased dependency on European loans and political concessions to European powers | |
It spurred a period of economic independence and self-sufficiency | |
It enhanced the empire's military alliances with Asian countries | |
It decreased European interest in Ottoman territories |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The financial instability and subsequent bankruptcy following the Crimean War forced the Ottoman Empire to rely heavily on European loans, which came with strings attached, including political and economic concessions. This dependency not only compromised the empire's sovereignty but also facilitated European meddling in its affairs, further weakening the empire's control over its territories and contributing to its eventual disintegration.
Question 15 |

What role did nationalist movements within the Ottoman Empire play in its decline and eventual dissolution?
They unified the empire's diverse populations under a single national identity | |
They exacerbated the empire's decline by seeking independence for various ethnic groups | |
They were largely unsuccessful and had little impact on the empire's stability | |
They strengthened the empire's central authority by promoting Ottomanism |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Nationalist movements within the Ottoman Empire, fueled by the desire of various ethnic and religious groups for self-determination, significantly undermined the cohesion and stability of the empire. These movements led to uprisings, contributed to internal discord, and weakened the central authority, making the empire more vulnerable to external pressures and interventions. This fragmentation was a key factor in the empire's gradual disintegration, culminating in its eventual dissolution after World War I.
Question 16 |
Questions 16–20 refer to the political cartoon below.

What does the "No Limit" cartoon from Puck in 1909 suggest about the global attitude towards naval expansion at the time?
Naval expansion was seen as a necessary measure for defense | |
There was a competitive nature in global powers building large navies | |
Naval expansion was primarily focused on promoting international trade | |
There was a global movement towards disarmament and peace |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The cartoon "No Limit" from 1909 captures the essence of the naval arms race that characterized the early 20th century, particularly among the United States, Japan, Germany, and other global powers. This period saw a significant increase in naval expenditure and shipbuilding, driven by the desire of these nations to assert their dominance and secure their interests on the global stage, often at the expense of escalating tensions and fostering an environment conducive to conflict.
Question 17 |

How did the naval arms race of the early 20th century contribute to the onset of World War I?
It decreased tensions between European powers through diplomatic negotiations | |
It led to significant advancements in naval technology that were purely defensive | |
It heightened tensions and created a climate of suspicion and rivalry among nations | |
It encouraged the formation of international alliances focused on trade |
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The naval arms race, particularly between Britain and Germany, significantly contributed to the buildup of tensions that eventually led to World War I. The competition for naval superiority fostered an atmosphere of mistrust and rivalry, as nations perceived the expansion of others' navies as direct threats to their own security and interests. This environment of heightened tensions and alliances, in turn, made the outbreak of war more likely.
Question 18 |

What role did technological advancements play in the naval arms race depicted in the "No Limit" cartoon?
They made navies obsolete through the development of air power | |
They fueled the competition as nations sought to outdo each other with more advanced and powerful ships | |
They led to a decrease in naval expansion due to the high costs of modernization | |
They encouraged nations to focus on diplomacy rather than military expansion |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Technological advancements played a crucial role in the naval arms race, as innovations in ship design, armament, and propulsion systems allowed for the creation of increasingly powerful and efficient warships. Nations invested heavily in these technologies to ensure their fleets remained competitive, further intensifying the arms race and the push for naval dominance.
Question 19 |

In what way did the naval expansion of the United States, as depicted in the "No Limit" cartoon, reflect the country's broader foreign policy goals?
It demonstrated its intention to become a global power | |
It indicated a shift towards isolationism and a focus on domestic issues | |
It showed the United States' commitment to peacekeeping and international cooperation | |
It reflected a preference for economic sanctions over military action |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The naval expansion of the United States during this period was part of a larger strategy to assert its presence on the world stage, protect its growing overseas territories and trade routes, and compete with other global powers for influence. This expansion was aligned with the broader foreign policy goals of projecting power and securing American interests abroad, as evidenced by actions like the Great White Fleet's world tour from 1907 to 1909.
Question 20 |

How did the naval expansions of Japan and Germany challenge the existing balance of power?
They encouraged smaller nations to undertake similar expansions, diluting the influence of larger powers | |
They led to an unprecedented era of peace and cooperation among naval powers | |
They diverted resources away from necessary economic reforms | |
They threatened the naval dominance of established powers like Britain |
Question 20 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The naval expansions of Japan and Germany represented a direct challenge to the naval supremacy of established powers, particularly Britain, which had long held a commanding lead in naval strength. These expansions not only threatened to alter the balance of power but also contributed to the global tensions and alliances that would eventually lead to World War I. Japan's victory in the Russo-Japanese War (1904–1905) and Germany's rapid naval buildup were clear indicators of their ambitions and the shifting dynamics of international power.
Question 21 |
Questions 21–25 refer to the photograph below.
Trenches of the 11th Cheshire Regiment in France, July 1916.
What aspect of World War I is highlighted by the image of the trenches of the 11th Cheshire Regiment in France, July 1916?
The mobility and fast-paced tactics of early 20th-century warfare | |
The static, grueling nature of trench warfare as a defining characteristic of the conflict | |
The technological advancements in naval warfare | |
The effectiveness of air raids in breaking the stalemate |
Question 21 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The image of the trenches underscores the brutal reality of trench warfare, which became emblematic of World War I. This form of warfare was characterized by its static nature, with soldiers living and fighting in trenches for extended periods, facing harsh conditions, and making little territorial gain despite significant losses.
Question 22 |
Trenches of the 11th Cheshire Regiment in France, July 1916.


How did the environment of the trenches impact the health and morale of soldiers during World War I?
It exposed soldiers to harsh living conditions, leading to diseases and a decline in morale | |
It provided a safe haven that boosted the soldiers' spirits | |
It encouraged rapid advancements in medical care and hygiene | |
It fostered a sense of camaraderie that outweighed the negative aspects |
Question 22 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The trench environment was notorious for its poor living conditions, including mud, waterlogging, vermin, and the constant threat of enemy fire. These conditions led to various health issues, such as trench foot, and contributed to a significant decline in morale among the troops.
Question 23 |
Trenches of the 11th Cheshire Regiment in France, July 1916.


What role did the trenches play in the strategic stalemate on the Western Front during World War I?
They were largely ineffective, leading to their abandonment early in the war | |
They allowed for rapid troop movements that prevented any stalemate | |
They made it difficult for either side to gain a decisive advantage, leading to a prolonged stalemate | |
They provided a launching point for successful cavalry charges |
Question 23 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The extensive use of trench warfare on the Western Front created a deadlock, with neither the Allies nor the Central Powers able to secure a significant breakthrough for much of the war. This network of defensive positions made it exceedingly difficult to advance without incurring heavy casualties.
Question 24 |
Trenches of the 11th Cheshire Regiment in France, July 1916.


In what ways did trench warfare influence post-war society and culture?
It left a lasting impact on the collective memory, leading to a strong aversion to war in society | |
It promoted the rapid development of urban infrastructure | |
It encouraged the continuation of trench warfare tactics in future conflicts | |
It diminished the perceived importance of infantry in military strategy |
Question 24 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The horrors and futility of trench warfare, as experienced by millions of soldiers, had a profound effect on post-war society and culture. The trauma and loss of life contributed to a widespread sense of disillusionment and a deep aversion to war, themes that were extensively explored in literature, art, and public discourse in the years following the conflict.
Question 25 |
Trenches of the 11th Cheshire Regiment in France, July 1916.


How did the use of trenches affect the development of military technology during World War I?
It spurred the development of new weapons and tactics designed to break the stalemate, such as tanks and poison gas | |
It led to the abandonment of heavy artillery in favor of more mobile weapons | |
It discouraged the use of aircraft in military operations | |
It reduced the need for innovations in naval warfare |
Question 25 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The static nature of trench warfare and the difficulty of breaching enemy lines led to significant innovations in military technology and tactics. The introduction of tanks aimed to cross no-man's land and overcome trench defenses, while poison gas was used in an attempt to flush out or incapacitate enemy soldiers in their trenches. These developments reflected the urgent need for solutions to the challenges posed by trench warfare.
Question 26 |
Questions 26–30 refer to the poster below.

What was the primary purpose of the British 1915 poster campaign "Turn Your Silver into Bullets at the Post Office"?
To encourage financial donations to support the war effort | |
To mobilize civilian resources for military production | |
To promote the recycling of household goods | |
To increase awareness of the war's economic impact |
Question 26 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The poster's call to "Turn Your Silver into Bullets" was a direct appeal to civilians to contribute materially to the war effort by donating silver, which could be used in the manufacture of ammunition. This campaign aimed to harness civilian support to bolster military supplies.
Question 27 |

How does the poster reflect the concept of "total war" during World War I?
It illustrates the direct involvement of military personnel in civilian life | |
It shows the integration of civilian contributions into the war effort | |
It highlights the role of technology in modern warfare | |
It emphasizes the importance of international alliances |
Question 27 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The concept of "total war" is characterized by the blurring of lines between civilian and military resources, with all aspects of society being directed towards the war effort. This poster exemplifies "total war" by encouraging civilians to contribute directly to military needs, thereby integrating civilian resources into the broader strategy of sustaining the war.
Question 28 |

What does the appeal to donate silver at the post office suggest about the British home front's role in WWI?
It underscores the critical role of civilian participation in supporting the war effort through material and financial contributions | |
It indicates a shortage of traditional funding sources for the war | |
It reflects a preference for non-monetary donations over financial contributions | |
It suggests a lack of governmental planning for war resources |
Question 28 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The campaign to collect silver for bullet production highlights how civilians were considered an essential part of the war effort, not just in terms of morale but also in providing the material support necessary to continue fighting. This initiative is indicative of the broader mobilization of the home front, where every contribution, no matter how small, was valued.
Question 29 |

In what way did the poster campaign "Turn Your Silver into Bullets" utilize propaganda techniques to support the war effort?
It appealed to civilians' sense of duty and patriotism to contribute materially to the war | |
It provided detailed information on the military's strategic needs | |
It emphasized the superiority of British military technology | |
It depicted enemy nations in a negative light |
Question 29 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The poster uses propaganda techniques by invoking a sense of national duty and patriotism, encouraging civilians to view their personal sacrifices as a direct contribution to the war effort. This emotional appeal is a common characteristic of wartime propaganda, aimed at mobilizing public support and resources for the military.
Question 30 |

What broader economic implications does the "Turn Your Silver into Bullets" campaign reveal about Britain during WWI?
It reveals a significant increase in the wealth of the average British citizen | |
It suggests that Britain was moving towards a barter economy due to the war | |
It implies that silver was more valuable as a raw material than as currency | |
It indicates the extensive economic mobilization and potential resource shortages faced by Britain |
Question 30 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The campaign to collect silver for ammunition production reflects the broader context of economic mobilization for the war effort, as well as the challenges of maintaining adequate supplies of essential materials. This initiative points to the lengths to which Britain was willing to go to ensure a steady supply of resources for the military, highlighting the economic strains and potential shortages that accompanied the prolonged conflict.
Question 31 |
Questions 31–35 refer to the map below.
The German Empire (1919–1935).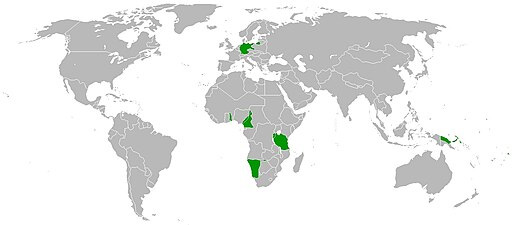
What significant geopolitical change in the German Empire is depicted in the above image from 1919 to 1935?
The expansion of the German Empire through colonial acquisitions | |
The territorial losses of the German Empire as a result of the Treaty of Versailles | |
The unification of German-speaking territories under a single empire | |
The division of the German Empire into East and West Germany |
Question 31 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The above image likely highlights the territorial adjustments imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles following World War I. This treaty significantly reduced Germany's territory and had profound implications for its national identity and geopolitical stance in the interwar period.
Question 32 |
The German Empire (1919–1935).


How did the territorial adjustments depicted in the above image impact Germany's economy in the interwar period?
They led to an economic boom due to reduced administrative costs | |
They contributed to economic hardship by stripping Germany of valuable industrial territories and resources | |
They had little impact as Germany quickly recovered through foreign investments | |
They encouraged economic diversification and innovation in new industries |
Question 32 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The territorial losses highlighted in the above image, particularly those of industrial regions and colonies, significantly weakened Germany's economy. The loss of resources, combined with reparations imposed by the Treaty of Versailles, exacerbated the economic challenges faced by Germany in the interwar period.
Question 33 |
The German Empire (1919–1935).


What role did the territorial changes shown in the above image play in the rise of nationalist movements in Germany?
They fueled nationalist and revanchist sentiments, contributing to the rise of movements seeking to overturn the post-war settlement | |
They diminished nationalist fervor by promoting a more cosmopolitan outlook | |
They had no significant impact on political ideologies in Germany | |
They encouraged the adoption of internationalism and cooperation with neighboring countries |
Question 33 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The territorial losses and the perceived humiliation of the Treaty of Versailles played a significant role in fostering nationalist and revanchist movements within Germany. These movements capitalized on public discontent and the desire to reclaim lost territories, which contributed to the political instability of the Weimar Republic and the eventual rise of the Nazi Party.
Question 34 |
The German Empire (1919–1935).


In what way did the territorial losses depicted in the above image influence Germany's foreign policy objectives in the lead-up to World War II?
They led Germany to adopt a more isolationist stance in international affairs | |
They motivated aggressive expansionist policies aimed at reclaiming lost territories and securing Lebensraum | |
They encouraged Germany to seek alliances with former enemies to prevent further territorial losses | |
They prompted Germany to focus on economic development and abandon territorial ambitions |
Question 34 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The territorial adjustments and the sense of grievance they engendered were central to Nazi foreign policy objectives, which included the revision of the Treaty of Versailles' terms and territorial expansion. These objectives were pursued through a combination of diplomatic maneuvers and military aggression, ultimately contributing to the outbreak of World War II.
Question 35 |
The German Empire (1919–1935).


How did the international community respond to the territorial changes in Germany depicted in the above image during the interwar period?
With a mix of approval, due to the desire to weaken Germany and prevent future conflicts, and concern over the potential for future instability | |
By offering economic aid to Germany to help it recover from the territorial losses | |
By pressuring Germany to further reduce its territory to ensure lasting peace | |
By largely ignoring the changes, focusing instead on other post-war issues |
Question 35 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The territorial adjustments made at the end of World War I were part of the Allies' broader strategy to weaken Germany and prevent it from posing a future threat. However, there was also concern among some in the international community that the harsh terms of the Treaty of Versailles, including significant territorial losses, might sow the seeds of future discontent and instability, rather than ensuring a stable and lasting peace.
Question 36 |
Questions 36–40 refer to the map below.
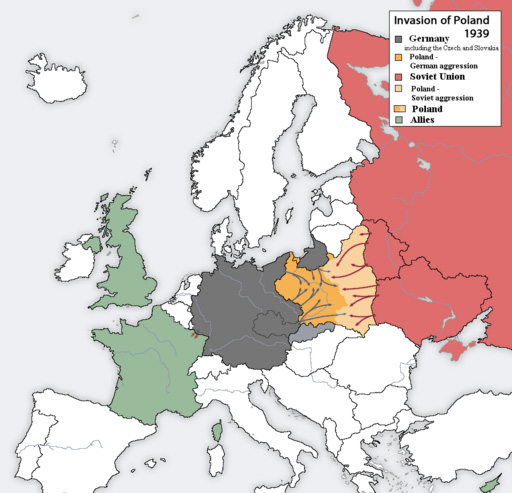
What does the depiction of Europe in 1939, specifically the invasion of Poland by the Nazis and the Soviets, signify in the context of World War II's outbreak?
The beginning of a prolonged period of peace in Europe | |
The conclusion of territorial disputes in Eastern Europe | |
A minor skirmish that had little impact on international relations | |
The event that marked the official start of World War II |
Question 36 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The invasion of Poland by Germany from the west and the Soviet Union from the east in September 1939 is widely recognized as the event that triggered the outbreak of World War II. This coordinated invasion resulted in the rapid defeat and partition of Poland, directly leading to Britain and France declaring war on Germany.
Question 37 |

How did the dual invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union reflect the political agreements between these two powers?
It demonstrated their long-standing alliance and shared ideologies | |
It indicated their mutual desire to combat Western imperialism | |
It was a result of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, a non-aggression treaty that included secret protocols for dividing Eastern Europe | |
It was an unintended consequence of their competition for dominance in the Balkans |
Question 37 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Signed in August 1939, the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union included secret protocols that outlined spheres of influence in Eastern Europe, leading to their joint invasion of Poland. This agreement temporarily aligned the interests of the two powers, despite their ideological differences.
Question 38 |

What was the immediate consequence of the invasion of Poland in 1939 for the Polish state and its citizens?
The establishment of a unified Polish-German-Soviet state | |
The division of Poland between Germany and the Soviet Union, leading to significant territorial losses and the beginning of occupation hardships for Poles | |
A quick recovery of Polish territories due to international intervention | |
The expansion of Poland's territory into neighboring countries |
Question 38 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The invasion resulted in the partition of Poland, with the west falling under German control and the east under Soviet control. This division led to the dissolution of the Polish state and subjected its citizens to brutal occupation regimes, including mass arrests, deportations, and the execution of civilians.
Question 39 |

In the broader context of European alliances and tensions, how did the invasion of Poland alter the diplomatic landscape?
It solidified the division between the Axis and Allied powers, leading to a full-scale European war | |
It encouraged a diplomatic resolution to territorial disputes in Eastern Europe | |
It led to a temporary truce between conflicting European nations | |
It isolated Germany and the Soviet Union from the rest of Europe diplomatically |
Question 39 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The invasion of Poland and the subsequent declarations of war by Britain and France against Germany marked a definitive end to hopes of appeasing Hitler and set the stage for the division of Europe into two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. This event crystallized the existing tensions into an open conflict that would engulf the continent.
Question 40 |

Reflecting on the strategic motivations behind the invasion, what objective did Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union aim to achieve through their actions in Poland?
A demonstration of military strength to potential allies | |
An expansion of their territories and security of their strategic positions in Eastern Europe | |
The establishment of a buffer zone against potential invasions from the West | |
A promotion of political stability and peace in the region |
Question 40 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Both Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union sought to achieve territorial expansion through the invasion of Poland. For Germany, the invasion was part of Hitler's broader ambitions for Lebensraum (living space) and the subjugation of Eastern Europe. For the Soviet Union, it was an opportunity to regain territories lost after World War I and to establish a buffer zone against future Western aggression.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 40 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Unit 8: Cold War & Decolonization >>
AP World History Main Menu >>
