Our APUSH unit 3 practice test includes 21 multiple choice questions. This period is marked by the struggle for independence and the birth of a new nation. The challenges of drafting foundational documents, and the debates that shaped them, such as those regarding federalism and individual rights, are central themes.
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Questions 1–3 refer to the following excerpt:
“Before those whom you call your brothers come on your lands, did you not live by bow and arrow? You had no need of gun nor powder, nor the rest of their things, and nevertheless you caught animals to live and clothe yourselves with their skins, but when I saw that you inclined to the evil, I called back the animals into the depths of the woods, so that you had need of your brothers to have your wants supplied and I shall send back to you the animals to live on.”
—Pontiac, an Ottawa war chief, 1763
—Pontiac, an Ottawa war chief, 1763
What goal did Pontiac try to achieve by making this speech?
He wanted to convert the Ottawa to Christianity to stop sin. | |
He wanted to create unity and cultural rejuvenation among indigenous peoples. | |
He wanted the Ottawa to become vegetarians. | |
He wanted to stop fratricide among the Ottawa. |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Pontiac resented the loss of traditional lifestyles among indigenous peoples as a result of prolonged contact with the colonists. He hoped unity would give the Native American people the strength to resist colonial expansion.
Question 2 |
“Before those whom you call your brothers come on your lands, did you not live by bow and arrow? You had no need of gun nor powder, nor the rest of their things, and nevertheless you caught animals to live and clothe yourselves with their skins, but when I saw that you inclined to the evil, I called back the animals into the depths of the woods, so that you had need of your brothers to have your wants supplied and I shall send back to you the animals to live on.”
—Pontiac, an Ottawa war chief, 1763
—Pontiac, an Ottawa war chief, 1763
What consequences did the French & Indian War have for indigenous peoples?
After the French victory they won full citizenship. | |
Nothing changed because it was a stalemate. | |
The British victory meant they all received full citizenship. | |
The British victory resulted in renewed pressure on tribal lands. |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The Proclamation of 1763 failed to stop colonial expansion and resulted in increasing pressure on Native American territory.
Question 3 |
“Before those whom you call your brothers come on your lands, did you not live by bow and arrow? You had no need of gun nor powder, nor the rest of their things, and nevertheless you caught animals to live and clothe yourselves with their skins, but when I saw that you inclined to the evil, I called back the animals into the depths of the woods, so that you had need of your brothers to have your wants supplied and I shall send back to you the animals to live on.”
—Pontiac, an Ottawa war chief, 1763
—Pontiac, an Ottawa war chief, 1763
How did colonists react to the Proclamation of 1763?
Many were angered and continued to settle illegally beyond the demarcation line. | |
Most colonists supported it because the proclamation ordered the expulsion of French settlers from Canada. | |
The colonists were unanimously disgusted because it ordered the colonies to convert to Catholicism. | |
Most supported it because it ordered the Native Americans to give up all their lands in North America. |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The Proclamation banned settlement beyond the Appalachian Mountains which created more tension and resentment between the colonies and the British crown.
Question 4 |
Questions 4–6 refer to the map below depicting the French and Indian War.
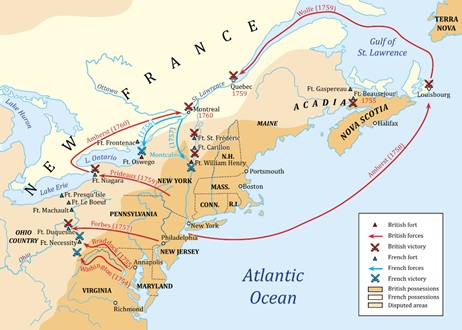
What important consequences did the French & Indian War have in North America?
None — the conflict ended in a stalemate. | |
The French victory forced the British king to abdicate. | |
The British victory expelled France from North America. | |
The British victory resulted in Spain taking over Canada. |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The French & Indian War radically altered the balance of power in North America.
Question 5 |

How did Britain try to deal with the massive expenses they incurred during the French & Indian War?
The British crown began to more rigorously enforce imperial policies and taxes. | |
The British king sold the crown jewels and all the other royal treasures. | |
The British empire sold all the colonies in North America to France. | |
The British cabinet forced the North American colonies to loan money to the crown. |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The colonies had become accustomed to the royal policy of salutary neglect and chafed under increasing imperial control.
Question 6 |

What role did the Native Americans play in the French and Indian War?
None — They stopped trading with both the French and British. | |
Indigenous peoples burned down Washington D.C. and the White House. | |
Although unanimously allied with the British, indigenous people fought in few battles. | |
Many Indigenous peoples sided with the French and attacked the British colonial frontier. |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Native Americans raided settlements and kidnapped many colonists. They initially had success but eventually ran out of ammunition.
Question 7 |
Questions 7–8 refer to the following excerpt:
“As to the history of the revolution, my ideas may be peculiar, perhaps singular. What do we mean by the revolution? The war? That was no part of the revolution; it was only an effect and consequence of it. The revolution was in the minds of the people, and this was effected from 1760 to 1775, in the course of fifteen years, before a drop of blood was shed at Lexington.”
—John Adams
—John Adams
Which of the following examples best supports Adams’ claim?
The Battle of Lexington & Concord because the Revolution only broke out after the colonies had won the war. | |
The Stamp Act because it helped unite the colonies. | |
Shay’s Rebellion because it helped inspired the Constitution. | |
The Boston Tea Party because it forced King George to sign the Declaration of Independence. |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The Stamp Act deepened the growing divide between the colonies and the British crown. The colonies complained they were being unfairly taxed and included this complaint against King George III in the Declaration of Independence.
Question 8 |
“As to the history of the revolution, my ideas may be peculiar, perhaps singular. What do we mean by the revolution? The war? That was no part of the revolution; it was only an effect and consequence of it. The revolution was in the minds of the people, and this was effected from 1760 to 1775, in the course of fifteen years, before a drop of blood was shed at Lexington.”
—John Adams
—John Adams
Which of the following statements best describes colonial attitudes during the Revolution?
Colonists overwhelming supported the Revolution — although a tiny minority opposed it. | |
A small minority supported it — the vast majority were indifferent. | |
Many colonists were patriots but there were also many loyalists and fence-sitters. | |
It is impossible to know because opinion polling did not yet exist. |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The actions of King George III and his cabinet turned many colonists into patriots. However, many remained loyal to the crown and thought the Revolution was an act of treason.
Question 9 |
Questions 9–10 refer to this map of battles during the American Revolution.
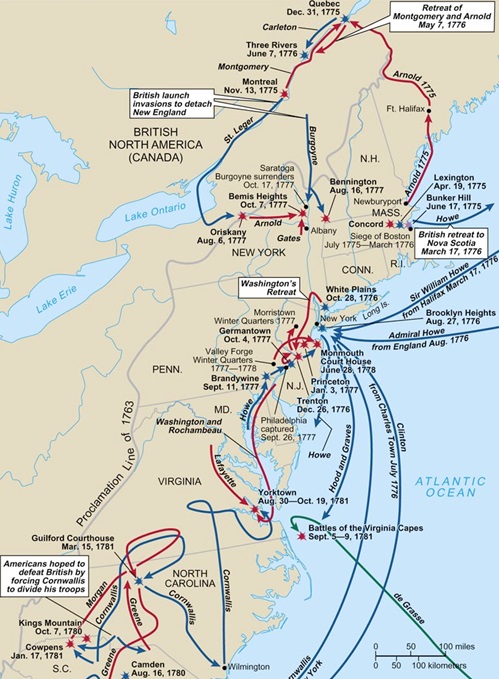
Which of the following statements best describes the course of the American Revolution?
The patriot forces eventually prevailed after a long and hard campaign. | |
All the important Revolutionary battles occurred in Massachusetts. | |
The small and professional British army was quickly overwhelmed by colonial forces. | |
At the time, it was impossible to know who was winning the war. |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Although well trained, the British forces were fighting far from home and needed lots of supplies. During a period of several years, the colonial forces became more efficient and reliable and were eventually able to defeat the British.
Question 10 |

What was the significance of the Battle of Saratoga in the autumn of 1777?
None — it ended in a stalemate. | |
It was a major British victory that crushed colonial hopes for a quick victory. | |
It was a pyrrhic colonial victory that prolonged the war. | |
It was a patriot victory that encouraged the French to support the revolution. |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The surrender of more than 6,000 British and Hessian troops demonstrated that the French would not back a losing army if they supported the patriots. French aid provided arms to the patriots and opened new theaters in the war.
Question 11 |
Questions 11–13 refer to the following excerpt:
“We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. — That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed, — That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness.”
—The Declaration of Independence
—The Declaration of Independence
What, if any, impact did the Enlightenment have on the American Revolution?
None — the Enlightenment was a religious movement. | |
Loyalists drew on Enlightenment ideals to refute the Revolution. | |
The Enlightenment was inspired by the Revolution. | |
The Enlightenment laid the foundation for the Revolution. |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The Enlightenment introduced many political ideals, such as natural rights, which helped shape the colonist’s complaints into the American Revolution.
Question 12 |
“We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. — That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed, — That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness.”
—The Declaration of Independence
—The Declaration of Independence
How did the Constitution address slavery?
The Founding Fathers banned slavery because it violated the ideals of the Revolution. | |
The Constitution included several compromises that legalized slavery. | |
The Constitution required that all slaves return to Africa. | |
The Constitution freed all slaves over the age of 18. |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The Constitution counted slaves as three-fifths of a person for the purposes of apportionment of taxation and representation.
Question 13 |
“We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. — That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed, — That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness.”
—The Declaration of Independence
—The Declaration of Independence
What, if any, influence did the Revolution have on world history?
None — slow trans-Atlantic communications meant that people in other regions never learned about the Revolution. | |
The Revolution had an immediate impact and lead to a massive wave of similar rebellions in every country in the world. | |
The ideals of the Revolution eventually inspired later movements in Latin America, the Caribbean, and France. | |
The Revolution forced monarchs in Europe to quickly make concessions in order to avoid similar uprisings. |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). European soldiers joined the Revolution and brought the ideals with them when they returned home. However, it took more than a decade before the French and Haitian Revolutions erupted, and Latin American idealists declared independence in the 19th century.
Question 14 |
Questions 14–16 refer to the following excerpt:
“There is nothing more common than to confound the terms of the American Revolution with those of the late American war. The American war is over: but this is far from being the case with the American Revolution. On the contrary, nothing but the first act of the great drama is closed. It remains yet to establish and perfect our new forms of government; and to prepare the principles, morals, and manners of our citizens, for these forms of government, after they are established and brought to perfection.”
—Benjamin Rush, signatory to the Declaration of Independence
—Benjamin Rush, signatory to the Declaration of Independence
Which of the following examples best supports Rush’s argument?
The transition from the Articles of Confederation to the Constitution. | |
Bacon’s Rebellion because it almost forced the revocation of the Bill of Rights. | |
The fact that no national government was established until after Cornwallis’ surrender at Yorktown. | |
The First Great Awakening because it taught Americans morals. |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The Articles of Confederation were signed during the Revolution and served as the first national government. The Articles of Confederation created a central government with very limited power and was eventually replaced by the Constitution which gave the national government more authority.
Question 15 |
“There is nothing more common than to confound the terms of the American Revolution with those of the late American war. The American war is over: but this is far from being the case with the American Revolution. On the contrary, nothing but the first act of the great drama is closed. It remains yet to establish and perfect our new forms of government; and to prepare the principles, morals, and manners of our citizens, for these forms of government, after they are established and brought to perfection.”
—Benjamin Rush, signatory to the Declaration of Independence
—Benjamin Rush, signatory to the Declaration of Independence
Which of the following issues would the Federalist Party have supported?
The Articles of Confederation. | |
The passage of the Constitution. | |
The need to protect individual liberty. | |
Opposition to the national bank. |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The Federalist Party thought the Articles of Confederation were too weak and that the Constitution would provide a stronger government. Federalists thought the executive should have more power than the legislature. They also felt a national bank would help control the American economy.
Question 16 |
“There is nothing more common than to confound the terms of the American Revolution with those of the late American war. The American war is over: but this is far from being the case with the American Revolution. On the contrary, nothing but the first act of the great drama is closed. It remains yet to establish and perfect our new forms of government; and to prepare the principles, morals, and manners of our citizens, for these forms of government, after they are established and brought to perfection.”
—Benjamin Rush, signatory to the Declaration of Independence
—Benjamin Rush, signatory to the Declaration of Independence
What position did Anti-Federalists take on the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights was unnecessary because the Constitution provided enough protections. | |
The Bill of Rights was illegal because the Constitution could not be altered. | |
The Bill of Rights was necessary in order to restrain the federal government. | |
The Bill of Rights actually was harmful because it gave more power to the federal government. |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The Anti-Federalists opposed the stronger federal government established by the Constitution and wanted a Bill of Rights in order to protect individual liberty and the power of state governments.
Question 17 |
Questions 17–18 refer to this painting from the late 18th century.
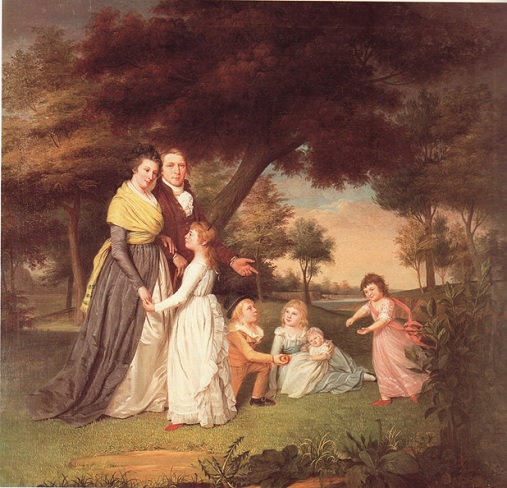

What political role did women play in the new American republic?
As mothers, they perpetuated republican ideals. | |
They unanimously opposed it because they could not vote. | |
They supported it because they enjoyed full equality. | |
None — they were completely uninterested in politics. |
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The concept of republican motherhood expected women to instill the values and ideals of the republic in their children, although they could not vote themselves.
Question 18 |

What economic role did women play in the new American republic?
Women had full equality and participated in every aspect of the economy. | |
American women refused to work at all until they received equal wages. | |
Women were generally paid less than men and rarely owned business. | |
None — women were not permitted to work. |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Women contributed to the economy in a variety of ways — particularly through the household. However, they did not have the same economic opportunities as men.
Question 19 |
Question 19–20 refers to the image below which depicts General Washington during the Whiskey rebellion (1791–1794).

What consequences did the Whiskey Rebellion have?
The rebellion was put down which helped secure the authority of the new national government created by the Constitution. | |
The rebellion nearly succeeded and thus hastened the end of the Articles of Confederation. | |
Massacres during the rebellion resulted in the passage of the Bill of Rights. | |
Washington was seriously wounded during the rebellion which led to the creation of the office of vice president in case the president died in office. |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The Constitution gave the federal government the power to quell the Whiskey rebellion, unlike the weak Articles of Confederation which was nearly undone by Shay’s Rebellion.
Question 20 |

Why is the presidential election of 1800 sometimes referred to as a “revolution?”
The electoral crisis led to the creation of the Constitution. | |
It was a peaceful transition from a Federalist to a Democratic-Republican administration. | |
It led to an armed conflict between the Federalists and Democratic-Republicans over control of the White House. | |
It was the first election in which women could vote. |
Question 20 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). After domination by Washington and the Federalist Party, Jefferson and the Democratic-Republicans were swept into power. It was a peaceful transition despite fears of civil war and insurrection.
Question 21 |
Question 21 refers to this image from the Battle of Fallen Timbers (1794):

Which of the following events helped secure American control over the future states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, and Wisconsin?
Victory in the Northwest Indian War. | |
Passage of the Northwest Ordinance. | |
Jay’s Treaty. | |
All of the above. |
Question 21 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The Northwest Ordinance provided for the settlement of the five future states, supported public education, and banned slavery in the new territories. Although suffering initial defeats, the US Army proved victorious at the Battle of Fallen Timbers in the Northwest Indian War. Jay’s Treaty forced the British to finally evacuate forts in the territory which they had promised to abandon after the Revolution.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 21 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Period 4 (1800–1848) >>
AP US History Main Menu >>
