Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A symbiotic relationship between two living organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped is known as:
Commensalism | |
Predation | |
Parasitism | |
Mutualism |
Question 2 |
Earthworms are a type of:
Scavenger | |
Parasite | |
Detritivore | |
Omnivore |
Question 3 |
At which trophic level are cheetahs located?
Producers | |
Primary consumers | |
Secondary consumers | |
Detritivores |
Question 4 |
In which of the following ecosystems is net primary productivity the highest?
Temperate forest | |
Savanna | |
Swamps and marshes | |
Temperate grassland |
Question 5 |
What percentage of biomass is conserved at each trophic level?
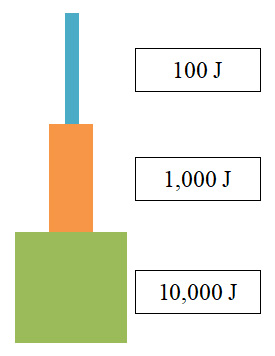
1% | |
5% | |
10% | |
20% |
Question 6 |
Which biogeochemical cycle depends on bacteria to make the nutrient usable by plants?
Nitrogen cycle | |
Carbon cycle | |
Phosphorus cycle | |
Water cycle |
Question 7 |
Which of the following terrestrial biomes is mostly made up of coniferous evergreen trees that can tolerate cold winters and short growing seasons, and is located in northern Europe, Russia, and North America?
Tundra | |
Boreal forest | |
Woodland/shrubland | |
Temperate seasonal forest |
Question 8 |
Which type of aquatic ecosystem is made up of salt-tolerant trees that are important in stabilizing tropical and subtropical coastlines?
Salt marshes | |
Intertidal zone | |
Mangrove swamps | |
Freshwater wetlands |
Question 9 |
At which level of complexity do different species interact with each other?
Ecosystem | |
Community | |
Population | |
Biome |
Question 10 |
What percentage of solar energy striking producers is captured by photosynthesis?
1% | |
5% | |
95% | |
99% |
Question 11 |
Which biogeochemical process is most impacted by burning fossil fuels?
Water cycle | |
Carbon cycle | |
Nitrogen cycle | |
Phosphorous cycle |
Question 12 |
Which of the following is released by volcanic eruption and is a necessary nutrient for living things but can also lead to acid rain?
Calcium | |
Potassium | |
Sulfur | |
Nitrogen |
Question 13 |
Which of the following biogeochemical processes has no atmospheric component?
Water cycle | |
Carbon cycle | |
Nitrogen cycle | |
Phosphorous cycle |
Question 14 |
Which biogeochemical cycle requires solar energy to move components from the earth into the atmosphere?
Water cycle | |
Phosphorus cycle | |
Nitrogen cycle | |
Carbon cycle |
Question 15 |
Which nutrient is a limiting nutrient in aquatic ecosystems and, when added to aquatic environments, typically causes algal blooms?
Hydrogen | |
Phosphorus | |
Potassium | |
Calcium |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
Which of the following tree species is a pioneer species in North American forests?
Beech | |
Aspen | |
Maple | |
Oak |
Question 2 |
Which of the following is the measurement used by ecologists to determine the biodiversity of a particular area?
Species richness | |
Species evenness | |
Genetic diversity | |
Ecosystem diversity |
Question 3 |
Which evolutionary process takes place when disturbance causes a dramatic decrease in the population size, causing the genetic composition of the survivors to substantially differ from the original group?
Mutation | |
Genetic drift | |
Founder effect | |
Bottleneck effect |
Question 4 |
At which level of complexity does evolution occur?
Ecosystem | |
Community | |
Population | |
Species |
Question 5 |
Which of the following factors does not influence species richness of a community?
Habitat size | |
Distance from other communities | |
The length of time the habitat has existed | |
The amount of biomass |
Question 6 |
Organisms need to acquire energy to survive. Which of the following are examples of adaptations that allow organisms to acquire the energy needed?
I. The long, slender beak of a hummingbird
II. The echolocation of a dolphin
III. The eyesight of an eagle
I only | |
II only | |
I and III | |
I, II, and III |
Question 7 |
Which of the following would be a cultural service of an ecosystem?
Timber produced by trees | |
Food items like nuts and berries | |
Hiking paths to enjoy nature | |
Air purification by native plants |
Question 8 |
Which of the following best describes why the ancestral finch species evolved into several distinct species after arriving on the islands?
Limited resources in the island ecosystems led to the adaptation of specialist traits to reduce competition between members of the species | |
An abundance of resources on the islands allowed the ancestral finches to be successful in filling all available niches | |
Reduced competition from other bird species allowed the finches to adapt to different food sources | |
Island climates tend to be more stable, which allowed the finches a consistent food source from year to year |
Question 9 |
According to the theory of island biogeography, which two characteristics of islands should determine the levels of biodiversity found on them?
Size and soil type | |
Distance to the nearest source of biodiversity and the number of islands in the area | |
Number of islands in the area and soil type | |
Size and distance to the nearest source of biodiversity |
Question 10 |
Which of the following is a likely impact of the slash-and-burn style removal of the Amazon rainforest?
Increased CFCs reducing atmospheric ozone | |
Increased carbon sequestration | |
Decreased soil erosion compared to traditional logging | |
Increased average global temperatures due to higher atmospheric CO2 |
Question 11 |
Giant tube worms live on the ocean floor near hydrothermal vents. This environment experiences temperatures far hotter than most organisms can withstand and contains a high concentration of toxic chemicals such as hydrogen sulfide that escape from the vents. Which of the following statements best explains why the giant tube worm can survive in this environment?
Competitors of the giant tube worm were wiped out by pollution, allowing the worms to dominate the ecosystem | |
The toxic environment near the vents led to a trophic cascade that eliminated tube worm predators | |
Giant tube worms are well adapted to the environment near the vents and can thrive there outside the range of tolerance of other organisms | |
Giant tube worms can survive in any environment, so it makes sense that they would fill an available niche |
Question 12 |
Based on the theory of island biogeography, why would a scientist expect to find less biodiversity on an island 25 kilometers from the mainland than on an island 8 kilometers from the mainland?
More species have the ability to travel to an island 8 kilometers away than to one 25 kilometers away | |
Islands closer to the mainland always have greater ecosystem diversity than islands further from the mainland | |
Islands further from the mainland normally have fewer available niches | |
Islands further from the mainland tend to see increased immigration as compared to islands closer to the mainland |
Question 13 |
A local ecologist has noticed that the population of bald eagles has fallen considerably over the past several years while other populations have remained stable. After running tests, the ecologist found that levels of DDT in fish in the area were extremely high. In this case, the bald eagles would be considered:
Pioneer species | |
Primary consumer | |
R-selected species | |
Indicator species |
Question 14 |
Urban barn swallows have adapted to live under the bridges of busy expressways in major metropolitan areas. Below is a group of measurements of wing length from a population of barn swallows living under bridges and a population of barn swallows living in a rural setting.
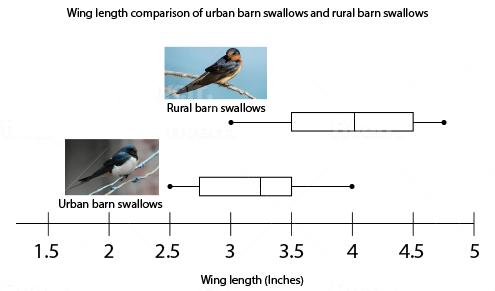
Which of the following can explain the difference in wing length seen between the two populations?
Rural barn swallows need longer wings to better navigate the more natural ecosystem they are found in | |
Urban barn swallows need shorter wings to better avoid the fast-moving traffic under the bridges, whereas longer wings would make them less maneuverable and more likely to be struck by cars | |
Rural barn swallows have accumulated a different set of random mutations that led to longer wings | |
Urban barn swallows do not live long enough to grow to the larger-sized wings of the rural barn swallows |
Question 15 |
Which of the following is the best example of a keystone species in a pond ecosystem?
Bluegill | |
Stork | |
Dragonfly | |
Beaver |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
Which of the following factors does NOT affect species richness?
Latitude | |
Survivorship curves | |
Time | |
Habitat size |
Question 2 |
In an experiment, two groups of paramecium species are grown together in a contained environment. P. aurelia grew well after 18 days, while P. caudatum declined to extinction over 18 days. This result demonstrates which of the following?
Competition | |
Predation | |
Competitive exclusion principle | |
Resource partitioning |
Question 3 |
A country has a net immigration rate of 3 per 1,000; a crude birth rate (CBR) of 9 per 1,000; and a crude death rate (CDR) of 11 per 1,000. What is the growth rate of this country?
0.1% | |
0.2% | |
0.5% | |
1% |
The national population growth rate is determined by calculating the difference between the factors contributing to population increase (CBR and immigration) and the factors contributing to population decrease (CDR and emigration), all divided by 10. Use the equation for national population growth:
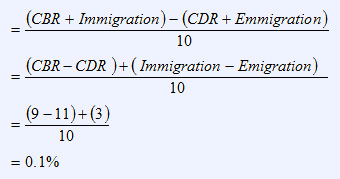
Question 4 |
Which of the following describes the shape of the logistic growth model with time as the independent variable and population growth as the dependent variable?
Parabolic curve | |
J-shaped curve | |
S-shaped curve | |
Straight line |
Question 5 |
Which of the following is an r-adapted species?
Elephants | |
Mice | |
Gorillas | |
Wolves |
Question 6 |
Which of the following population descriptions portrays the number of individuals in a particular age category?
Population size | |
Population density | |
Population distribution | |
Population age structure |
Question 7 |
Questions 7-9 refer to the following graphs:
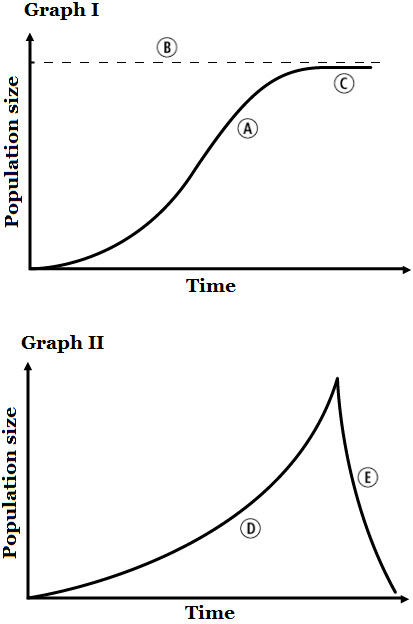
Which example fits the growth pattern shown in Graph II?
A population of 10 rabbits is introduced into an area with a good supply of food that regenerates easily | |
A population of 4 coyotes is reintroduced into an area that previously sustained a population of several hundred coyotes before they were hunted to local extinction | |
A population of reindeer was introduced to an island with no predators and a limited food supply; after the food was consumed, there was a dramatic drop in the population size | |
A population of harbor seals was actively hunted in Washington state in the early 20th century under a government program that viewed them as harmful predators, greatly reducing their numbers; since the program was discontinued, the seal population has rebounded in a logistic pattern |
Question 8 |

Which letter on the graphs represents a population’s carrying capacity?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 9 |

Which letter on the graph represents exponential growth?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 10 |
The average number of offspring required to offset the average number of deaths in a population so that the population remains stable is referred to as:
Crude birth rate | |
Crude death rate | |
Replacement level fertility | |
Total fertility rate |
Question 11 |
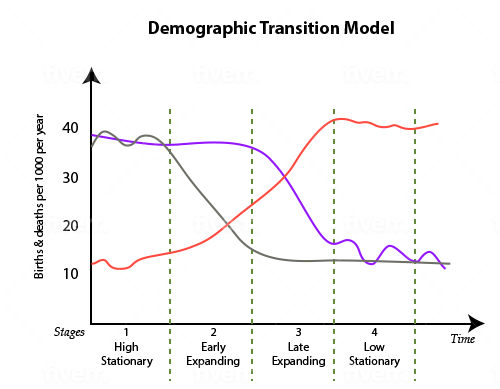
Question 11 refers to the following graph:
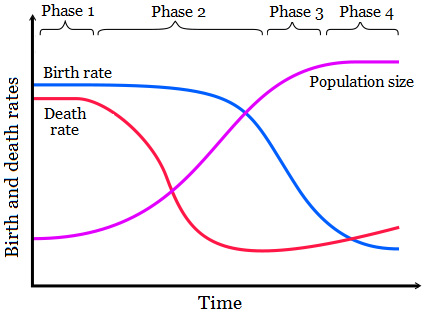
During which phase(s) of the demographic transition does the death rate decline while the birth rate remains high, causing the population to grow rapidly?
Phase 1 | |
Phase 2 | |
Phase 3 | |
Phase 4 |
Question 12 |
Question 12 refers to the following age structure diagram:
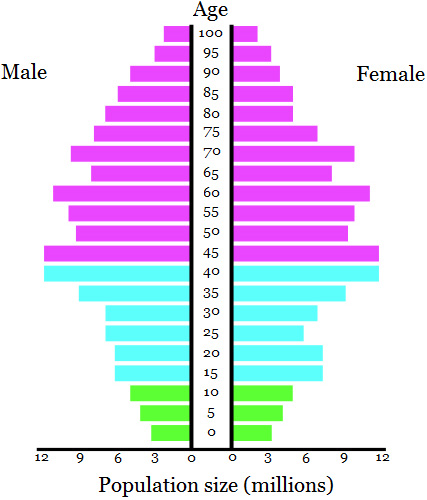
A country with an age structure like the one shown above will experience:
A rapidly growing population | |
Stable population growth | |
A decline in population | |
High life expectancy |
Question 13 |
Which of the following illustrates a global impact related to population growth?
Traffic into cities creates traffic jams and increases travel time into and out of developments | |
The conversion of forested areas into agricultural land reduces the uptake of carbon dioxide by plants | |
Converting land into agricultural land causes erosion | |
The building of new developments decreases habitat for local wildlife |
Question 14 |
Which line on the chart CORRECTLY matches the traits for K-selected and r-selected species?
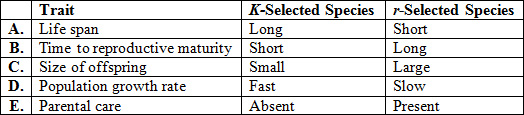
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 15 |
Racoons are found in urban, suburban, rural, and wild settings. Because they can make use of a wide range of habitats and resources, they are considered:
Producers | |
Omnivores | |
Keystone species | |
Generalists |
Question 16 |
A factor that influences an individual's ability to survive and reproduce based on the size of a population in a given area is known as a:
Carrying capacity | |
Limiting resource | |
Density-independent factor | |
Density-dependent factor |
Question 17 |
A country with a high birth rate and a high death rate, where many children are born but few people make it to middle and old age, has an age structure diagram that looks like what?
A tapered column | |
A column | |
An inverted pyramid | |
A pyramid
|
Question 18 |
According to the theory of demographic transition, a population in phase four would show which type of population growth?
Declining population growth | |
Stable population growth | |
Rapid population growth | |
Slow population growth |
Question 19 |
Type I survivorship curves show that the number of survivors remains stable early but eventually decreases sharply at a particular upper age limit. Type II survivorship curves show that the number of survivors steadily decreases with an increase in age.
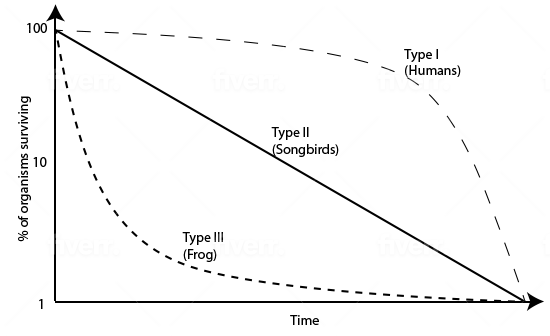
Which of the following can you determine from the descriptions of survivorship curves provided above?
Type II could represent an r-selected species with few surviving offspring | |
Type II could represent a K-selected species with few offspring that each have a high chance of survival | |
Type I could represent a prey animal with few offspring surviving to adulthood | |
Type II could represent a species that is in the middle of the r to K selection spectrum, such as a rabbit |
Question 20 |
Which of the following factors lead(s) to a declining birth rate in countries transitioning from phase two to phase three in the demographic transition model?
I. More women tend to stay home as a country becomes more developed, leading to decreased birth rates
II. More women tend to earn advanced degrees in developed nations, so they enter the workforce and have less time to raise children
III. There are more opportunities to own businesses in developed nations
I is correct | |
I and III are correct | |
I and II are correct | |
II and III are correct |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
An area beneath the ocean floor where tectonic plates move away from each other is known as a:
Subduction zone | |
Divergent plate boundary | |
Convergent plate boundary | |
Transform fault boundary |
Question 2 |
Which of the following layers of the earth is entirely liquid?
Inner core | |
Outer core | |
Mantle | |
Lithosphere |
Question 3 |
The loss of some or all of a soil’s ability to support plant growth is called
Erosion | |
Soil degradation | |
Physical weathering | |
Chemical weathering |
Question 4 |
Which list orders soil types from least to most organic content?
Young soil, immature soil, mature soil | |
Immature soil, young soil, mature soil | |
Mature soil, immature soil, young soil | |
Mature soil, young soil, immature soil |
Question 5 |
Which list shows the layers of the atmosphere in order, starting with the layer closest to earth?
Stratosphere, troposphere, mesosphere, thermosphere | |
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere | |
Stratosphere, troposphere, thermosphere, mesosphere | |
Troposphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere |
Question 6 |
Which of the following correctly lists the layers of the earth from the innermost layer to the outside layer?
Solid inner core, liquid outer core, mantle, crust | |
Liquid outer core, solid inner core, mantle, crust | |
Solid inner core, liquid outer core, crust, mantle | |
Crust, mantle, liquid outer core, solid inner core |
Question 7 |
Which type of plate interaction occurs when plates move sideways past each other?
Fault zone | |
Divergent plate boundary | |
Convergent plate boundary | |
Transform plate boundary |
Question 8 |
Which soil horizon is composed mainly of mineral material with very little organic matter?
O horizon | |
A horizon | |
B horizon | |
D horizon |
Question 9 |
The percentages of the soil’s sand, silt, and clay is referred to as:
Texture | |
Minerals | |
Horizons | |
Relative particle size |
Question 10 |
Where is the greatest amount of fresh water located on Earth?
Water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and ponds | |
The atmosphere | |
Oceans | |
Ice and glaciers |
0.04% atmospheric water
0.3% surface water
30% ground water
68+% ice and glaciers
Question 11 |
Which of the following atmospheric layers is the closest to the earth?
Thermosphere | |
Troposphere | |
Mesosphere | |
Stratosphere |
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Exosphere
Question 12 |
What could a farmer do to prevent crop loss due to heavy rains waterlogging his crops?
The farmer could amend his soil with clay to decrease porosity | |
The farmer could use contour plowing to prevent soil erosion | |
The farmer could use cover crops to increase organic material in the soil | |
The farmer could amend his soil with sand to increase porosity |
Question 13 |
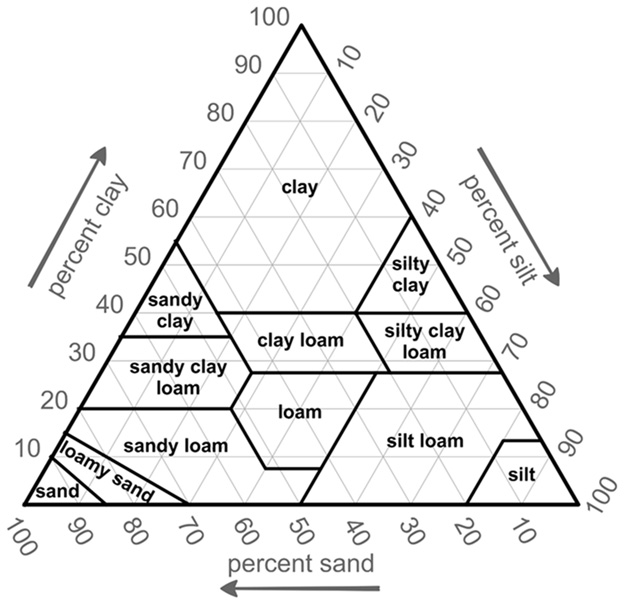
In the image above, which category would soil fall into if it is 30% sand, 10% clay, and 60% silt?
Silty clay | |
Loam | |
Silt Loam | |
Sandy Loam |
Question 14 |
Which layer of the Earth’s atmosphere contains the highest percentage of water vapor?
The troposphere | |
The stratosphere | |
The mesosphere | |
The thermosphere |
Question 15 |
Which is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume?
CO2 | |
CH4 | |
O2 | |
N2 |
Question 16 |
Soybeans require soil that drains well to grow well. Which type of soil would be best to farm soybeans in?
Soil that contains at least 45% clay so that it retains plenty of water | |
Soil that contains at least 80% silt due to its low amounts of sand | |
Sandy loam that contains less than 20% clay | |
Silty clay loam because it contains all three soil components |
Question 17 |
Which of the following has the greatest effect on the global distribution of solar energy that leads to seasons?
The tilt of the Earth’s axis concerning the sun | |
The curvature of the Earth | |
The shape of the Earth's orbit | |
The location of the Earth’s landmasses |
Question 18 |
Which agricultural practice would most likely lead to lower turbidity in nearby rivers and streams?
Using crop rotation in fields | |
Removing excess vegetation surrounding crop fields | |
Using synthetic fertilizers | |
Changing fields from crops to cattle pasture |
Question 19 |
Though Iceland and Greenland are found at similar latitudes in the North Atlantic Ocean, Iceland sees a considerably warmer average daily temperature year round and is not covered by glaciers the way that Greenland is. Which of the following best explains the difference in the climates of Greenland and Iceland?
Solar radiation reaching Greenland is of higher intensity, leading it to more readily reflect off of the glaciers found there | |
Oceanic currents from equatorial regions flow around the coast of Iceland, helping to warm the atmosphere | |
The people living in Iceland have altered the climate to be more suitable | |
Polar air currents move at greater speeds over Greenland, stripping away much of the heat there |
Question 20 |
Dams are built to regulate flooding downstream and occasionally to produce hydroelectric power. Which of the following is a negative environmental impact of building a dam on a river?
Sediment is prevented from flowing downstream, which can lower the productivity of portions of the river past the dam as well as any wetlands found at the mouth of the river | |
A new habitat will form behind the dam that can increase recreational spending in the area | |
More regulated flow downstream will stabilize the banks of the river | |
Local human populations will benefit from the increase in green, renewable energy |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
If a deep well pumps water from an aquifer more rapidly than it can be regenerated, which of the following may form?
Cone of depression | |
Saltwater intrusion | |
Confined aquifer | |
Unconfined aquifer |
Question 2 |
Which of the following is the most efficient method of irrigation?
Drip | |
Flood | |
Spray | |
Furrow |
Question 3 |
Deforestation can lead to:
Adverse soil erosion | |
Desertification | |
Extinction | |
All of the above |
Question 4 |
Which of the following is a disadvantage of mono-cropping?
I. Soil depletion
II. Large expanses of land can be planted and then harvested
III. Crops are more vulnerable to attacks by pests
I only | |
II only | |
I and II only | |
I and III only |
Question 5 |
What is bycatch?
A environmental problem caused by increased pesticide use. | |
Raising fish commercially in tanks or enclosures, usually for food. | |
Unwanted fish and other marine creatures caught during commercial fishing for a different species. | |
A common side effect of genetic engineering. |
Question 6 |
The phenomenon of urban blight has contributed to which of the following?
I. Degradation of the buildings and social environment of the city
II. Migration to the suburbs
III. Racial segregation
I only | |
II only | |
I and III only | |
I, II, and III |
Question 7 |
Which of the following is a benefit of contour farming?
Allows vegetation of different heights to act as windbreaks and catch soil that might otherwise blow away | |
Prevents the same nutrients from being removed from the soil year after year | |
Conserves soil and prevents erosion | |
Reduces carbon dioxide emissions |
Question 8 |
Which of the following is a benefit of genetic engineering?
Genetic engineering decreases the likelihood of an allergic reaction to a specific type of food | |
The favorable genes in the genetically modified organism will spread to wild varieties and increase their ability to resist disease | |
Genetically modified organisms are healthier because their genes have been selected to make the crop more nutritious for humans | |
Genetically modified organisms need less pesticides because the plants have been developed to resist pests |
Question 9 |
Abandoned coal mines can lead to which of the following environmental problems?
Increased photochemical smog from ozone seeping from the mine | |
Acid rain from increased SO2 | |
Acid leaching from leftover mine tailings | |
Released nutrients leading to eutrophication of nearby waterways. |
Question 10 |
Which of the following is a reason why biological control methods are not favorable to traditional pesticides?
Biological controls tend to target only one species where pesticides can kill beneficial organisms. | |
Biological controls do not add harmful chemicals that can spread into the local waterways because of run-off. | |
Crop loss to pests with biological controls is typically higher than crop loss with traditional pesticides. | |
Pests tend to adapt and become more resistant to traditional pesticides over time. |
Question 11 |
Which of the following is NOT an environmental advantage of urbanization?
Less land is used per individual as compared to rural settings. | |
Lack of permeable surfaces causes a depletion of groundwater resources. | |
Individuals may be able to walk where they need to go or make use of public transportation to reduce fossil fuel reliance. | |
Less power is used per person as larger buildings are more efficient in retaining heat in the winter and cool in the summer. |
Question 12 |
It takes 20 times more land to produce beef than it does to produce corn. If corn can produce 1000 Kcal per hectare, how much land would it take to produce 5000 Kcal of beef?
20 hectares | |
100 hectares | |
200 hectares | |
2000 hectares |
Question 13 |
Which is likely why we have exceeded the maximum sustainable yield in ocean fisheries?
There are now too many marine fish farms | |
Interspecific competition is limiting population recovery in fish. | |
Too many reproductive-aged fish are being harvested yearly. | |
Climate change has negatively impacted fisheries. |
Question 14 |
Which piece of legislation is most effective at addressing the problems with overfishing?
The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act gives instructions on the management of aquatic resources. | |
The Delaney Clause of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act regulates the harvesting of fish for human consumption. | |
The Clean Water Act regulates the dumping of pollutants into surface waters. | |
The Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) of wild fauna and flora uses trade rules to protect commercially valuable species. |
Question 15 |
What type of changes would be expected to be seen in a local hydrologic cycle as a result of clearcutting regional forests?
Siltation of local waterways will decrease | |
Transpiration from vegetation will increase | |
Runoff from watersheds will decrease | |
Evaporation from the soil will increase |
Question 16 |
If a society wanted to be more sustainable they would:
Use energy more efficiently and reduce and reuse resources whenever possible. | |
Maintain current rates of energy consumption and resource use. | |
Convert the world's high energy resources into low-quality heat. | |
Use more nuclear power because it is a renewable resource. |
Question 17 |
Which commercially used forestry method is most likely to cause fragmented landscapes and have negative impacts on biodiversity?
Slash and Burn | |
Shelter-wood cutting | |
Clear-cutting | |
Selective Cutting |
Question 18 |
| Farm A | Farm B | |
| Animal Waste | Manure reused as fertilizer | Manure stored in lagoons |
| Average days in barn per year | 0 days | 45 days |
| Antibiotic use | Only when sick | Routinely to prevent spread of infection |
Based on the table above, which best describes the two farms above?
Farm A is a free-range farm for cattle while farm B is a traditional CAFO for cattle. | |
Farm A is a free-range farm for chickens and farm B is a free-range farm for cattle. | |
Farm A is a free-range farm for chickens and farm B is an industrial poultry farm. | |
Farm A is a traditional CAFO for Cattle and farm B is a free-range farm for cattle. |
Question 19 |
Of the following which, would be an unintended environmental impact of aquaculture?
Increased production of fish for market. | |
Concentrated organic waste in the surrounding water. | |
Decreased disease in the native fish population. | |
High cost of building the facility. |
Question 20 |
Which is a true statement about genetic diversity?
GM crops with decreased genetic diversity are better able to survive a changing environment. | |
Genetic diversity in a common crop such as soy beans is typically high. | |
Genetic resistance to disease can be increased by crossing crops with related varieties. | |
Genetic diversity is typically high in small populations. |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A stair-like structure that allows migrating fish to navigate through a dam is known as a(n)
Fish Ladder | |
Aqueduct | |
Dike | |
Levee |
Question 2 |
The largest renewable source of electricity generation in the United States is
Wind | |
Solar | |
Geothermal | |
Hydroelectric |
Hydro 44%
Wind 37%
Biomass 10%
Solar 6%
Geothermal 3%
Question 3 |
Which of the following pairs is the predominant source of fuel for electricity generation in the United States?
Natural Gas and Oil | |
Oil and Coal | |
Nuclear fuels and Solar Power | |
Coal and Natural Gas |
Question 4 |
Which of the following is NOT one of the advantages of natural gas as an energy source?
Burning it releases no pollutants. | |
It is efficient for cooking and home heating. | |
It is abundant. | |
It can be stored and transported. |
Question 5 |
Currently, most high-level radioactive waste from nuclear reactors in the United States is
stored in deep ocean trenches. | |
reprocessed into new fuel pellets. | |
chemically modified into safe materials. | |
stored at the power plant that produced it. |
Question 6 |
Which of the following is true of passive solar designs?
These designs use mechanical and electrical devices for heating and cooling. | |
These designs have windows, walls, and floors that are made to collect, store, and distribute solar energy in the form of heat in the winter, and reject solar heat in the summer. | |
These designs have solar hot water systems which use pumps or fans to circulate fluid. | |
These designs use low-impact building materials and permeable concrete instead of conventional concrete to enhance the replenishment of ground water. |
Question 7 |
Which of the following nonrenewable energy sources accounts for 68% of the CO2 that is emitted by the U.S. electric power sector?
Coal | |
Oil | |
Natural gas | |
Nuclear power |
Question 8 |
Which type of coal has the lowest energy content?
Bituminous | |
Lignite | |
Anthracite | |
All of these have equal energy content |
Coal starts as peat. After a long amount of time, heat, and burial pressure, it is metamorphosed from peat to lignite. Lignite is called "immature" coal at this stage of development because it is rather light in color and remains soft. As time passes, lignite increases in maturity by becoming darker and harder and is then classified as sub-bituminous coal. With more time, pressure, and heat, more chemical and physical changes occur and the coal is classified as bituminous. At this point, the coal is dark and hard. Anthracite is the last of the classifications when the coal has matured completely. Anthracite coal is very hard and shiny.
Question 9 |
Which of the following nonrenewable energy sources is easily transported through establishing pipelines, produces a high net-energy yield, is subsidized by the U.S. government, and can be used to produce many other products such as paints, medicines and plastics?
Coal | |
Oil | |
Natural gas | |
Nuclear power |
Question 10 |
Which of the following nonrenewable energy sources produces less SO2 and NOx than other fossil fuels when burned, leading to less of an impact on acid rain and photochemical smog?
Coal | |
Oil | |
Natural gas | |
Hydroelectric |
Question 11 |
In which part of a nuclear power plant is the fuel located?
Core | |
Cooling tower | |
Turbine | |
Electrical generator |
Question 12 |
Which of the following is an advantage of nuclear power?
There is enough uranium left for the next 100,000 years | |
Nuclear wastes are easily recyclable | |
Uranium is a renewable resource | |
Nuclear power generation produces very little water pollution |
Question 13 |
Which of the following is an example of an active solar heating system?
Putting reflective coatings on roofs and exterior walls | |
Increasing insulation | |
Using photovoltaic solar cells to absorb solar energy | |
Installing skylights to allow sunlight into the building |
Question 14 |
Which of the following is the fastest growing source of electricity in the world?
Hydrogen fuel cells | |
Wind energy | |
Geothermal energy | |
Hydroelectricity |
Question 15 |
A family in Chicago wants to install solar panels on the roof of their house to help lower the electric bill. Which direction should the solar panels face for the best possible results?
North | |
East | |
South | |
West |
Question 16 |
In less developed countries, which fuel source is most commonly used for heating and cooking?
Coal | |
Oil | |
Natural Gas | |
Biomass |
Question 17 |
Cars produce roughly 20 pounds of CO2 per gallon of gasoline burned.
If one person drives 30,000 miles in a car that averages 30 miles per gallon, while another drives 30,000 miles in a car that averages 20 miles per gallon, how many fewer pounds of CO2 were produced by the first car?
1000 | |
10,000 | |
60,000 | |
600,000 |
Question 18 |
Which of the following is a negative environmental consequence of using photovoltaic solar cells?
Photovoltaic cells produce high amounts of NOx pollution while generating electricity. | |
Photovoltaic cells are responsible for stratospheric ozone depletion. | |
Photovoltaic cells are made using toxic metals that may get into the environment. | |
Photovoltaic cells contribute to the formation of tropospheric ozone and photochemical smog. |
Question 19 |
A home uses five 100-watt lightbulbs for six hours per day. How many kilowatt-hours of energy are used per year by using those lightbulbs?
1095 | |
10,950 | |
3,650 | |
36,500 |
Question 20 |
The extraction of natural gas is likely to have which negative impact on the environment?
Ozone Depletion | |
Photochemical Smog formation | |
Eutrophication | |
Groundwater contamination |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
Which of the following is an example of a secondary pollutant?
Ozone | |
Carbon Monoxide | |
Carbon Dioxide | |
Sulfur Dioxide |
Question 2 |
The Montreal Protocol was signed in 1987 by 24 countries to regulate:
substances that cause air pollution. | |
substances that deplete the ozone layer. | |
indoor air quality. | |
the amount of smog in ppm in the air. |
Question 3 |
The process of recycling a product into the same product is known as:
solid waste recycling | |
open-loop recycling | |
closed-loop recycling | |
reuse recycling |
Question 4 |
Which of the following is considered a point source of water pollution?
Sewage treatment plant discharging wastewater form a pipe into the ocean | |
Erosion from agricultural areas | |
Storm runoff from parking lots | |
Fertilizers from a golf course |
Question 5 |
Which of the following sources of hazardous substances contaminate water when drinking water passes through pipes in older homes and can potentially damage the nervous system and kidneys?
Arsenic | |
Lead | |
Mercury | |
Acid deposition |
Question 6 |
Which air pollutant bonds to hemoglobin, resulting in reduced air transport in the bloodstream?
Nitrogen oxides | |
Carbon monoxide | |
Carbon dioxide | |
Ozone |
Question 7 |
What group of organisms is most affected by acid deposition?
Amphibians | |
Terrestrial mammals | |
Reptiles | |
Birds of prey |
Question 8 |
Which of the following indoor air pollutants is a type of radioactive gas that seeps into a home through cracks in the foundation or soil, and may cause lung cancer?
Asbestos | |
Carbon monoxide | |
Radon | |
VOCs |
Question 9 |
Which ingredient was removed from gasoline, and has significantly reduced the amount found in the atmosphere?
Carbon monoxide | |
Nitrogen oxide | |
Organic compounds | |
Lead |
Question 10 |
What is a concentration of 20 ppm equivalent to?
0.2% | |
0.02% | |
0.002% | |
0.0002% |
Question 11 |
Which is the strongest piece of evidence that a local area was experiencing acid deposition?
An increase in the amount of soluble heavy metals in a local pond. | |
A sudden die-off of all fish in a pond. | |
A gradual increase in the temperature of a local lake. | |
An increase in the diversity of micro-invertebrates in a local lake. |
Question 12 |
The average vehicle produces 1.39 grams of NOx per mile driven. If a truck is driven 32,000 miles per year for 12 years, how much NOx will that truck release?
534 grams | |
44,480 grams | |
444,800 grams | |
533,760 grams |
1.39 grams × 32,000 miles × 12 years = 533,760 grams
Question 13 |
This substance is composed of fibers and is known to cause lung cancer:
Radon | |
Lead | |
Asbestos | |
Carbon Monoxide |
Question 14 |
This substance is emitted from manufactured building materials, furniture, and adhesives:
Radon | |
Formaldehyde | |
Asbestos | |
Lead |
Question 15 |
A pond in southern Canada had a pH of 8.2 in 1950, and by 1990 it’s pH had fallen to 5.6. Which of the following would be a short-term remediation strategy for the pond?
Change the pond ecosystem by introducing fish more tolerant of the lower pH. | |
Install barriers to prevent runoff from emptying into the pond. | |
Add calcium carbonate to the pond water. | |
Build taller smokestacks downwind from the pond. |
Question 16 |
Which of the following is a natural source of CO2 in the atmosphere?
Photosynthesis by plants and plankton | |
Sedimentation of rock on the ocean floor | |
Decomposition of organic matter | |
Erosion of bedrock |
Question 17 |
This toxin poses a risk to humans who eat large amounts of marine game fish:
Radon | |
Lead | |
Copper | |
Mercury |
Question 18 |
The presence of which of the following in soil is most likely to mitigate the effects of acid rain?
Granite | |
Limestone | |
Sand | |
Humus |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
Consumption of which hazardous material is known to affect the thyroid gland?
Lead | |
DDT | |
Mercury | |
Perchlorates |
Question 2 |
The legislation that sets the national standards for safe drinking water is known as the:
Clean Water Act. | |
Safe Drinking Water Act. | |
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. | |
Federal Water Pollution Control Act. |
Question 3 |
What is the purpose of the leachate collection system in a modern sanitary landfill?
Extract methane produced for use as fuel. | |
Prevent additional water from entering the landfill. | |
Remove water and contaminants for treatment at a wastewater treatment plant. | |
Impede water flow from the landfill and retain positively charge ions such as metals. |
Question 4 |
Which of the following is the most controversial method for oil spill cleanup?
Contain the spill using booms, and collect the oil from the surface of the water using skimmers | |
Use chemical dispersants to break down the oil | |
Add biological agents to the spill | |
Let the oil breakdown naturally |
Question 5 |
Superfund is the common name given to which federal law?
The Clean Air Act | |
The Clean Water Act | |
The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act | |
The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act |
Question 6 |
Electronic waste such as cathode ray tube televisions and computer monitors may contain this toxic metal.
Cadmium | |
Aluminum | |
Copper | |
Titanium |
Question 7 |
Which Act is the principal federal law governing the disposal of solid waste and hazardous waste?
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act | |
Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act | |
Toxic Substances Control Act | |
Occupational Safety and Health Act |
Question 8 |
The increasing concentration of a toxic substance in the tissues of organisms at successively higher levels of the food chain is known as:
Biomagnification | |
Bioaccumulation | |
Biodilution | |
Bioconcentration |
Question 9 |
Which type of carcinogenic synthetic organic compound were manufactured in plastics and insulating electrical transformers until 1979, and even though they are no longer manufactured in the United States, they are still present in the environment?
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane | |
Perchlorates | |
Polychlorinated biphenyls | |
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers |
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, or DDT, is an insecticide designed to target nerve transmissions in pests. It was found that DDT moved up the aquatic food chain up to eagles, causing eagles to produce thin shells that broke before the embryo developed.
Perchlorates are used for rocket fuel and are easily leached from contaminated soil into the groundwater where they can persist for many years. Perchlorates can affect the thyroid gland and reduce important hormone production.
Polybrominated diphenyl (PBDEs) ethers are flame retardants added to a variety of items including construction materials, furniture, and clothing. Since the 1990s, scientists have been detecting them in fish, aquatic birds, and human breast milk. Exposure to some types of PBDEs can lead to brain damage. Several states, including Washington and California, have banned the manufacture of several types of PBDEs. Pharmaceuticals are not components of plastics and insulating electrical transformers.
Question 10 |
Which of the following contributes to thermal pollution?
Geothermal energy production | |
Hydroelectric energy production | |
Cultural eutrophication | |
Electric power plants |
Question 11 |
During the process of sewage treatment, which stage removes large objects, such as leaves, diapers, tampons, and wet-wipes?
Pretreatment | |
Primary Treatment | |
Secondary Treatment | |
Tertiary Treatment |
Question 12 |
Which group of harmful chemicals interfere with the normal functioning of hormones in an animal’s body?
Neurotoxins | |
Carcinogens | |
Endocrine Disruptors | |
Allergens |
Question 13 |
Which of the following is an example of solid waste pollution?
Sediment | |
Oil | |
Mercury | |
Garbage |
Question 14 |
All of the following might be used to reduce the effects of eutrophication in a lake EXCEPT:
Adding Nitrates | |
Dredging the lake to make it deeper. | |
Introducing insects to consume nuisance plants | |
Pumping oxygen into the lowest layers of the water |
Question 15 |
Which is an example of a non-point source of pollution?
Dumping from a processing plant | |
Exhaust pipe from a generator | |
Outflow from a waste treatment plant | |
Agricultural runoff |
Question 16 |
Testing the tissues of an average US citizen would likely show the presence of DDT. DDT was banned in 1972. Why would DDT still be found in people today?
Newer pesticides break down into DDT and then enter the ecosystem | |
Other countries still use DDT on their crops | |
DDT is water-soluble | |
DDT is naturally occurring in many bodies of water |
Question 17 |
Bioaccumulation occurs because:
The substance is fat-soluble and will build up in tissues faster than it is removed. | |
Organisms tend to consume more of the substance than other things. | |
The substance is water-soluble and quickly removed from an organism. | |
The substance is beneficial to organisms lower on the food chain. |
Question 18 |
LD50 refers to:
The dose at which a toxin harms 50% of the individuals in a population. | |
The length of time needed for a drug work on individuals in a population. | |
The dose at which 50% of exposed individuals die in a population. | |
The length of time needed for 50% of exposed individuals to die in a population. |
|
List |
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
Which of the following greenhouse gases is the longest-lasting in the atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide | |
Methane | |
Nitrous oxide | |
Chlorofluorocarbons |
Question 2 |
Which of the following is NOT a greenhouse gas?
Carbon dioxide | |
Water vapor | |
Nitrogen | |
Methane |
Question 3 |
Which of the following has the greatest Global Warming Potential (GWP)?
Carbon dioxide | |
Methane | |
Nitrous oxide | |
Fluorinated gases |
Question 4 |
Which of the following is a potential result of higher average air temperatures?
Increase in the frequency or severity of storms | |
Increases in the surface water and/or groundwater inputs | |
Increases in flooding and associated water runoff | |
All of the above |
Question 5 |
The melting of glaciers causes which of the following?
Landslides | |
Flash floods | |
Displacement of people who depend on glacial melting as a water source | |
All of the above |
Question 6 |
The International Union for Conservation of Nature uses five categories to define the status of a species. Which category refers to a group of species that is widespread and abundant?
Extinct | |
Threatened | |
Near-threatened | |
Least concern |
Question 7 |
In the 1600s, honeybees (Apis melifera) were introduced to North America to provide a source of honey for European colonists. This makes honeybees a(n):
Native species | |
Exotic species | |
Threatened species | |
Invasive species |
Question 8 |
What causes biodiversity loss worldwide?
Pollution | |
Habitat loss | |
Climate change | |
All of the above |
Question 9 |
Which greenhouse gas is correctly paired with its source?
Carbon dioxide; burning coal and oil | |
Chlorofluorocarbons; fire extinguishers | |
Nitrous oxide; cellular respiration | |
Methane; plastic manufacturing |
Question 10 |
Over the past 100 years, global temperatures have:
increased, with virtually of all the increase occurring in the last 40 years | |
fluctuated within a narrow range, with no net increase | |
increased, with most of the increase occurring from 1940 to 1980 | |
decreased steadily, before a sharp increase in the last 20 years |
Question 11 |
Which of the following agreements was designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the global production of numerous substances which cause ozone depletion?
Clean Air Act | |
Kyoto Protocol | |
Paris Agreement | |
Montreal Protocol |
The Clean Air Act was passed in 1963 and was designed to control air pollution on a national level.
The Kyoto Protocol was a plan created by the United Nations that tries to reduce the effects of climate change.
The Paris Agreement set out a global action plan to put the world on track to avoid dangerous climate changes.
The Air Pollution Control Act addressed air pollution as a national problem and announced that research and additional steps to improve the situation needed to be taken.
Question 12 |
Which of the following was the 1992 UN treaty to reduce greenhouse gases through binding emission reduction targets on developed countries?
Clean Air Act | |
Kyoto Protocol | |
Paris Agreement | |
Montreal Protocol |
Question 13 |
Which of the following was the 2016 UN agreement on greenhouse gas emissions, allowing each country to determine, plan, and report on its contribution with no enforcement mechanism?
Clean Air Act | |
Kyoto Protocol | |
Paris Agreement | |
Montreal Protocol |
Question 14 |
Which of the following is NOT a naturally occurring greenhouse gas?
Methane | |
Nitrous oxide | |
Chlorofluorocarbons | |
Carbon dioxide |
Question 15 |
What was the primary purpose of reintroducing wolves to Yellowstone in the 1990s?
Restore the natural ecosystem of the park by keeping herbivores in check and allowing plant life to recover | |
Introduce a competitor for the coyotes because they were dominating the ecosystem | |
Attract more tourists to view the wolves | |
Protect livestock that inhabits the outer edges of the park |
Question 16 |
Which of the following is NOT a possible impact of global warming?
Disease vectors will find increased ranges as the climate warms near the poles | |
Flood plains used to grow crops will be under water due to sea level rise | |
Areas now suitable for agriculture will become even more productive | |
People will need to migrate to new regions as local water supplies are disrupted |
Question 17 |
Why are HCFCs NOT a permanent solution to protect the stratospheric ozone layer?
They are just as useful as refrigerants but not in sprays | |
HCFCs do not harm the ozone layer but do contribute to global warming | |
HCFCs do not contribute to global warming but do harm the ozone layer | |
HCFCs still harm the ozone layer, just not as much |
Question 18 |
Ozone depletion occurs naturally over Antarctica during which season?
Spring | |
Summer | |
Fall | |
Winter |
Question 19 |
Human activities increase the rate of evaporation of water into the atmosphere, but anthropogenic water vapor does not contribute to climate change because:
Water vapor does not absorb and re-radiate infrared | |
Water vapor is not a greenhouse gas | |
Heat absorbed by water vapor is only directed back out to space | |
Water vapor has a short residence time in the atmosphere |
Question 20 |
Increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will impact marine organisms in what way?
pH will decrease outside the range of tolerance for most marine organisms | |
Water temperature will decrease, causing marine organisms to migrate towards the equator | |
There would be decreased availability of bicarbonate ions, making it harder for corals and shellfish to grow their shells | |
There would be increased availability of bicarbonate ions, making it harder for corals and shellfish to grow their shells |
Question 21 |
Which would likely lead to an increase in the acidity of the oceans?
Increased burning of fossil fuels for power generation. | |
Decrease in deforestation for agriculture. | |
Increase in primary productivity of terrestrial ecosystems. | |
Increase in the use of public transportation. |
Question 22 |
This greenhouse gas can be found in the lower troposphere due to photochemical reactions.
H2O | |
CO2 | |
O3 | |
CH4 |
Question 23 |
Which of the following is a contributor to both global warming and depletion of the ozone layer?
Increased CO2 in the atmosphere from burning fossil fuels. | |
Release of CFCs into the atmosphere. | |
Increased levels of UV light reaching the surface of the Earth. | |
Increased methane in the atmosphere from pre-industrial levels. |
Question 24 |
Which of the following would likely have the greatest positive impact on ecosystems globally?
Stabilization or reduction of the size of the human population. | |
Increased agricultural production in marginal farming communities. | |
Increased life expectancy in developing nations. | |
Discovery of more fossil fuel reserves in arctic regions. |
Question 25 |
The data shows global sea levels have risen in the last 100 years. Which of the following factors best explains why this has happened?
Increased precipitation. | |
Melting permafrost. | |
Increased evapotranspiration. | |
Thermal Expansion. |
Question 26 |
If average global temperatures continue to rise as predicted, which of the following is most likely?
The geographical range of plants will move towards the equator. | |
There will be a decline in pests and disease-carrying vectors near the poles. | |
Specialist species will be at greater risk of extinction | |
Specialist species will be at a lesser risk of extinction. |
Question 27 |
Which of the following best describes the process involved in the greenhouse effect?
Ozone absorbs UV light from the sun warming the stratosphere. | |
Absorption of infrared radiation by atmospheric gases in the troposphere. | |
Diffusion of visible light by aerosols. | |
Breakdown of oxygen in the thermosphere. |
Question 28 |
An area of temperate forest will be partially cleared to build a new subdivision. The developers will leave some sections of forest intact to preserve as much of the native ecosystem as possible. Which is the likely impact of the removal of much of the forest ecosystem?
An increase in large predators making use of more vulnerable prey populations. | |
A decrease in the rate of soil erosion in the area. | |
An increase in the rate of primary productivity in the area. | |
A reduction of specialist species due to smaller habitats. |
Question 29 |
The most likely cause of species extinction in the future is likely:
Habitat loss | |
Hunting and poaching | |
Weaker environmental legislation | |
Aggressive collection for museums and zoos |
Question 30 |
Scientists theorize that increased carbon dioxide in the oceans could be harmful to certain fish species. They suspect immature fish are more at risk due to the increased carbon dioxide. Which of the following could be a good, testable hypothesis to test this theory?
Increased carbon dioxide in the water will lead to denser skeletons in mature fish. | |
Decreasing the pH of the water will lower fish larvae survival rates. | |
Decreasing the temperature of the water will lead to lower fish larvae survival rates. | |
There will be a greater number of fish larvae that survive than mature fish that survive. |
|
List |
