Below is our free AP US Government unit 1 practice test. This unit is called Foundations of Democracy. It covers types of democracy, government power, individual rights, founding documents such as the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution, and federalism.
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which of the following is NOT expressed in the Declaration of Independence?
Natural rights | |
Popular sovereignty | |
Separation of powers | |
The social contract |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The Declaration of Independence explains why the American Revolution happened. It does not set up branches of government.
Natural or unalienable rights (A) are listed as “life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.” Popular sovereignty (B) is found in “Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed.” The social contract (D) is found in the phrase “That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government.”
Natural or unalienable rights (A) are listed as “life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.” Popular sovereignty (B) is found in “Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed.” The social contract (D) is found in the phrase “That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government.”
Question 2 |
Which of the following comparisons is correct?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 2 Explanation:
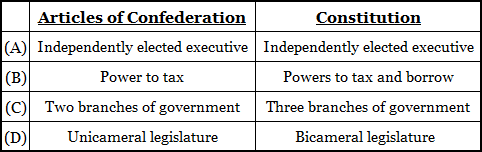
The correct answer is (D). All of the powers in the Constitution column are part of the Constitution. Under the Articles of Confederation, the president was elected by Congress and had almost no power, so answer (A) may be eliminated. Congress did not have the power to tax, which rules out answer (B), and there was only one branch of government, the legislature, which rules out answer (C). The legislature consisted of a unicameral congress under the Articles of Confederation, so answer (D) is correct.
Question 3 |
Which of the following events indicated that the Articles of Confederation needed to be strengthened?
The Battle of Yorktown | |
The election of 1785 | |
Shays’ Rebellion | |
The Whiskey Rebellion |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Many prominent Americans agreed that the Articles of Confederation should be strengthened when the governments of Massachusetts and the United States were unable to halt Shays’ Rebellion. Later, after the Constitution was adopted, the new, stronger government stopped the Whiskey Rebellion, demonstrating that the new Constitution could be effective.
Question 4 |
Article V of the Constitution illustrates
Federalism | |
Judicial review | |
Limited government | |
Popular sovereignty |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Article V is the constitutional amendment process, which normally requires a two-thirds majority in each house of Congress and the approval of three-quarters of the states. Thus, power is divided “federally,” between the Congress and the states.
Question 5 |
Questions 5–7 refer to the chart below:
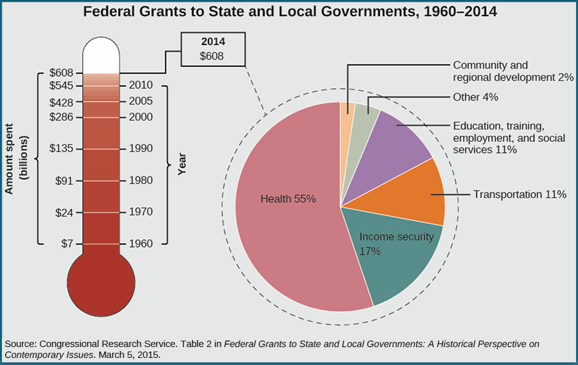
Based on the chart above and what you know about United States government, which of the following is true?
Federal grants to state and local governments have increased at a rate greater than the rate of inflation | |
Federal grants to state and local governments have increased at about the same rate as inflation | |
Federal grants to state and local governments have increased at a rate lower than the rate of inflation | |
Federal grants to state and local governments have not increased at all |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Inflation has increased annually at an average rate of 3.75 percent since 1960, but the graph on the left shows grants increasing at a far greater rate.
Question 6 |

The largest section of the pie chart probably goes to support
Insurance subsidies | |
Medicare | |
Medicaid | |
Veterans benefits |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Medicaid is a federally-funded state-run healthcare program. Medicare (B) and the Veterans Administration (D) are both run by the federal government. Insurance subsidies (A) do not relate to the question.
Question 7 |

In order to receive the grants shown above, states and localities would have to agree to
Block grants | |
Dual federalism | |
Discretionary grants | |
Conditions of aid |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Conditions of aid in federal grants refer to the requirements or stipulations that recipients must fulfill in order to receive and retain the grant funds.
Block grants (A) come without conditions of aid and can be used by state and local governments for almost anything. Dual federalism (B) is a form of federalism in which the state and federal governments have divided responsibilities. Discretionary grants (C) are competitive and based on merit.
Block grants (A) come without conditions of aid and can be used by state and local governments for almost anything. Dual federalism (B) is a form of federalism in which the state and federal governments have divided responsibilities. Discretionary grants (C) are competitive and based on merit.
Question 8 |
An impeachment hearing is an example of
Checks and balances | |
Popular sovereignty | |
Rule of law | |
Separation of powers |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). In an impeachment hearing, Congress puts a check on the president, the vice president, high-level officers of the executive branch, or judges.
Question 9 |
How do most strict constructionists feel about the Patriot Act and other surveillance laws passed by Congress since the 9/11 terrorist attacks?
They support such laws because the federal government should have a strict response to terrorism | |
They support such laws because the Constitution puts the federal government in charge of national defense | |
They do not support such laws because they believe states should be in charge of homeland security | |
They do not support such laws because surveillance of American citizens is not explicitly listed as a power of Congress in the Constitution |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Strict constructionists believe the federal government should be limited to powers that are expressly stated in the Constitution.
Question 10 |
Which of the branches of government did James Madison and Alexander Hamilton predict would be strongest? Which branch did they predict would be weakest?
Legislative; Executive | |
Legislative; Judicial | |
Executive; Legislative | |
Executive; Judicial |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The answer is derived from several writings, but in particular, it draws from The Federalist No. 51 and The Federalist No. 78. There are also clues found in the Constitution itself; Article I is much longer than Article III and lists specific powers delegated to Congress, which was done to keep Congress from overreaching its authority. Finally, George Washington limited his use of the veto to legislation that he thought was unconstitutional. The executive branch is now much more powerful than it was in the eighteenth century. Interestingly, the Anti-Federalists accurately predicted that the executive branch would grow in power.
Question 11 |
Which of the following statements is the most accurate description of the Great (Connecticut) Compromise?
It created the electoral college | |
It allowed Congress to ban the importation of slaves after twenty years | |
It gave equal consideration to both the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan | |
It accepted many of the provisions of the Virginia Plan but retained an upper house of Congress based on equality among the states |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The Great (Connecticut) Compromise settled the debate over representation, which eliminates answers (A) and (B). The Great Compromise did not accept the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan equally. The Great Compromise accepted most provisions of the Virginia Plan, including a bicameral legislature. The New Jersey Plan included a unicameral legislature in which each state had one vote.
Question 12 |
In James Madison’s view, a large republic
Was a democracy | |
Was based on majority rule | |
Would prevent a tyranny of the majority | |
Would stretch from the Atlantic Ocean to the Appalachian Mountains and possibly further west |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Madison opposed democracy (A) because, in a pure democracy, the majority could take away the rights of a minority. Hence, majority rule (B) was also something Madison was against. The United States government is not based on majority rule; it is based on majority rule with minority rights. Answer (D) is the definition of manifest destiny.
Question 13 |
In Contrast to most European countries, the United States government
Is based on a written constitution | |
Operates quickly and efficiently | |
Operates slowly and deliberately | |
Shares fewer powers with subordinate governments |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Every country in Europe except the United Kingdom has a written constitution, so answer (A) may be eliminated. The United States government is based on a federal system, so answer (D) may also be eliminated. Due to separation of powers and checks and balances, it is difficult for one branch of government to act without the approval of at least one of the other branches. Therefore, answer (C) is correct. Answer (B) is the opposite of (C).
Question 14 |
Which of the following comparisons is correct?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 14 Explanation:
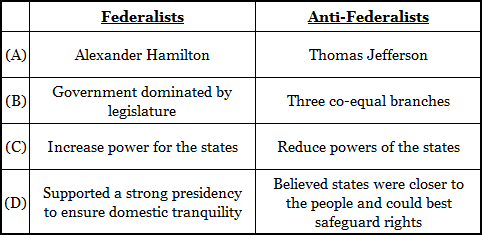
The correct answer is (D). According to Brutus No. 1, the states were closer to the people and could, therefore, best safeguard the people’s rights.
Hamilton and Jefferson both supported the Constitution and were, thus, both Federalists before the Federalists became a political party. Jefferson was never an Anti-Federalist. Therefore, answer (A) may be eliminated. Answers (B) and (C) are reversed.
Hamilton and Jefferson both supported the Constitution and were, thus, both Federalists before the Federalists became a political party. Jefferson was never an Anti-Federalist. Therefore, answer (A) may be eliminated. Answers (B) and (C) are reversed.
Question 15 |
Which of the following comparisons is correct?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 15 Explanation:
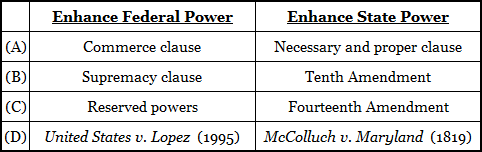
The correct answer is (B). The commerce clause, the supremacy clause, and reserved powers grant powers to Congress. They helped move the United States from a Confederation of states to a unified country under a federal system of government. The necessary and proper clause (also known as the elastic clause) also strengthened the powers of Congress, so answer (A) may be eliminated. The equal protection clause of the Fourteenth Amendment (C) has been interpreted by the Supreme Court so that almost every part of the Bill of Rights now applies to the states, which effectively weakens state authority restrict civil rights and liberties. Thus, answer (C) may be eliminated. United States v. Lopez ruled federal gun-free school zones unconstitutional and, thus, returned some power to the states. Answer (D), therefore, may be eliminated. The Tenth Amendment says, “The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.” It, therefore, enhances state power.
Question 16 |
Which of the following scenarios would be considered an unconstitutional use of state power?
California creates a single-payer healthcare system | |
New York places a tax on cranberries imported from Massachusetts | |
Texas puts extra law enforcement officers along its border with Mexico | |
Wisconsin decreases the drinking age to 19 years of age |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). States are not allowed to place tariffs on goods made outside their borders. Under the Tenth Amendment, a state may create a healthcare system for its residents (A). A state may place state law enforcement officers almost anywhere within its borders (C). One might think answer (D) is correct; however, the 21-year-old drinking age is not a federal law. A state can opt for a lower drinking age if it does not mind losing its federal highways funds. Currently, all fifty states have a 21-year-old drinking age.
Question 17 |
Questions 17–20 refer to the passage below:
If a faction consists of less than a majority, relief is supplied by the republican principle, which enables the majority to defeat its sinister views by regular vote. It may clog the administration, it may convulse the society; but it will be unable to execute and mask its violence under the forms of the Constitution. When a majority is included in a faction, the form of popular government, on the other hand, enables it to sacrifice to its ruling passion or interest both the public good and the rights of other citizens. To secure the public good and private rights against the danger of such a faction, and at the same time to preserve the spirit and the form of popular government, is then the great object to which our inquiries are directed. Let me add that it is the great desideratum by which this form of government can be rescued from the opprobrium under which it has so long labored, and be recommended to the esteem and adoption of mankind.
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
Which of the following comes closest to Madison’s notion of a faction?
Bureaucratic agency | |
Interest group | |
Military interest | |
Political party |
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Federal bureaucratic agencies did not exist at the time The Federalist Papers were published. The United States had no standing army under the Articles of Confederation, so answer (C) is unlikely. The bureaucracy was not envisioned by Madison (A). Political parties (D) are mentioned and were considered a type of faction at the time, but answer (B) is the more inclusive answer.
Question 18 |
If a faction consists of less than a majority, relief is supplied by the republican principle, which enables the majority to defeat its sinister views by regular vote. It may clog the administration, it may convulse the society; but it will be unable to execute and mask its violence under the forms of the Constitution. When a majority is included in a faction, the form of popular government, on the other hand, enables it to sacrifice to its ruling passion or interest both the public good and the rights of other citizens. To secure the public good and private rights against the danger of such a faction, and at the same time to preserve the spirit and the form of popular government, is then the great object to which our inquiries are directed. Let me add that it is the great desideratum by which this form of government can be rescued from the opprobrium under which it has so long labored, and be recommended to the esteem and adoption of mankind.
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
By what means do factions safeguard people’s rights?
Factions promote democracy | |
Factions promote republicanism | |
Factions encourage government to act against the interests of the people | |
Factions discourage government from acting against the interests of the people |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Madison did not support democracy (A), the rule of the people. He did support a republican form of government (B), but factions do not promote republicanism. Rather, republicanism encourages factions. Answer (C) is the opposite of (D). the government has a hard time acting when different factions compete for power; therefore, the government has a difficult time violating people’s civil rights.
Question 19 |
If a faction consists of less than a majority, relief is supplied by the republican principle, which enables the majority to defeat its sinister views by regular vote. It may clog the administration, it may convulse the society; but it will be unable to execute and mask its violence under the forms of the Constitution. When a majority is included in a faction, the form of popular government, on the other hand, enables it to sacrifice to its ruling passion or interest both the public good and the rights of other citizens. To secure the public good and private rights against the danger of such a faction, and at the same time to preserve the spirit and the form of popular government, is then the great object to which our inquiries are directed. Let me add that it is the great desideratum by which this form of government can be rescued from the opprobrium under which it has so long labored, and be recommended to the esteem and adoption of mankind.
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
Which of the following theories of government comes closest to the main point of The Federalist No. 10?
Bureaucratic | |
Elite | |
Participatory | |
Pluralistic |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Pluralism involves many different groups competing for power and/or influence. The bureaucratic view (A) is the theory that bureaucratic agencies control government. The elite view (B) involves just a few key players. Participatory democracy (C) emphasizes the broad participation of constituents in the direction and operation of political systems.
Question 20 |
If a faction consists of less than a majority, relief is supplied by the republican principle, which enables the majority to defeat its sinister views by regular vote. It may clog the administration, it may convulse the society; but it will be unable to execute and mask its violence under the forms of the Constitution. When a majority is included in a faction, the form of popular government, on the other hand, enables it to sacrifice to its ruling passion or interest both the public good and the rights of other citizens. To secure the public good and private rights against the danger of such a faction, and at the same time to preserve the spirit and the form of popular government, is then the great object to which our inquiries are directed. Let me add that it is the great desideratum by which this form of government can be rescued from the opprobrium under which it has so long labored, and be recommended to the esteem and adoption of mankind.
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
—James Madison, The Federalist No. 10
Which of the following Constitutional amendments most directly protects the activities of factions?
First | |
Second | |
Fourth | |
Ninth |
Question 20 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Interest groups are protected by the First Amendment rights to assemble as well as freedom of speech and the press. The Second Amendment (B) is the right to bear arms. The Fourth Amendment (C) protects against unreasonable search and seizure. The Ninth Amendment (D) protects the rights of the people that are not explicitly mentioned elsewhere in the Constitution.
Question 21 |
A person is accused of assaulting a police officer in Montana. The person returned to Indiana before the assigned trial date. The governor of Montana asked the governor of Indiana to send the accused back to Montana to stand trial. This procedure is known as
The Full Faith and Credit Clause | |
Extradition | |
Writ of habeas corpus | |
Ex post facto law |
Question 21 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Extradition involves transferring from one state to another to stand trial. The Full Faith and Credit Clause (A) allows recognition of public Acts, Records, and judicial Proceedings, but does not address returning accused individuals to a state to stand trial. A writ of habeas corpus (C) is used to determine if detaining an individual is lawful. Ex post facto law (D) is retroactively changing the legal consequences of an action.
Question 22 |
The paradox of democracy can best be described as
How to solve the issue of federalism | |
The potential of double taxation from the federal and state governments | |
Taxation without representation | |
The conflict between majority rule and individual freedom |
Question 22 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). One of the most well-known paradoxes of democracy is known as the “tyranny of the majority.” This paradox suggests that in a democratic society where decisions are made through majority rule, there is a risk that the majority may oppress or marginalize minority groups, thereby undermining the principles of equality and individual rights that democracy is meant to uphold.
Question 23 |
The picket fence metaphor is an apt description of current American federalism because
States require federal money to create policy, while the federal government follows their lead | |
Policymakers mainly interact with others in the same policy area, regardless of whether they are federal or state employees | |
Chief executives such as mayors, governors, and the president have few powers over the legislative branch | |
The state and federal governments often have clear boundaries within specific policy areas |
Question 23 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). “Picket fence federalism” is used to describe a model of federalism where intergovernmental relations are structured around specific policy areas rather than just levels of government. In this model, various levels of government (federal, state, and local) collaborate horizontally across policy areas, resembling the image of picket fences arranged side by side rather than a strict hierarchy of authority.
Question 24 |
Because the Constitution only sets broad boundaries for state and federal powers, the ________ is vital in resolving disputes over powers in specific instances.
President | |
Tenth Amendment | |
Supreme Court | |
Federal Government |
Question 24 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Through its power of judicial review, the Court has the authority to interpret the Constitution and determine the boundaries of state and federal authority. The Court's decisions establish precedents that guide future interpretations of the Constitution and clarify the respective powers of state and federal governments, helping to maintain the balance of power envisioned by the framers of the Constitution.
Question 25 |
When the national government gives the states money to entice them to change state laws to match national goals or policies established by Congress, this is an example of what kind of federalism?
National federalism | |
Dual federalism | |
Implied federalism | |
Fiscal federalism |
Question 25 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Fiscal federalism is one level of government withholding or providing money or resources to a different level of government with a goal of influencing governmental behavior. Dual federalism (B) describes clear boundaries of responsibilities among levels of government in a policy area. The other terms are not commonly identified forms of federalism.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 25 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Unit 2: Branches of Government >>
AP US Government Main Menu >>
