AP Human Geography unit 6 transitions from rural land-use to urban land-use, as well as the infrastructure, challenges, and distribution of urban communities worldwide. The 15 questions below will help prepare you for the urban concepts featured on the AP exam.
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
A large city with a high level of consumer services, a significant number of international company headquarters, and a polarized social structure is a
forward capital | |
global city | |
hypercity | |
megacity | |
megalopolis |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). This question involves memorizing vocabulary. Global cites are also known as “world cities.” A forward capital is a symbolically relocated capital city usually because of either economic or strategic reasons. Hypercities and megacities are found in less-developed countries. A megalopolis is an integrated collection of cities.
Question 2 |
If a country has a city that has a disproportionately larger share of a country’s population compared to the second largest city, then the country follows the
imperial city rule | |
primate city rule | |
rank-size rule | |
Rostow model | |
Wallerstein model |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). This question also involves memorizing vocabulary. Imperial city is a fictitious term in the context of the question, and neither of the models apply. The rank-size rule is a system by which the cities in a country are ranked in order of size and a proportional to that rank.
Question 3 |
Place the following retail nodes in the correct order from oldest to most recent:
central business district, “big box” superstore, shopping mall, internet | |
central business district, shopping mall, “big box” superstore, internet | |
central business district, shopping mall, internet, “big box” superstore | |
shopping mall, “big box” superstore, central business district, internet | |
shopping mall, central business district, “big box” superstore, internet |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Central business districts were the primary places for shopping until the development of shopping malls in the 1970s. “Big box” superstores, such as Walmart, became popular in the 1990s. All brick-and-mortar retailors have been losing ground to electronic commerce since the early 2000s.
Question 4 |
Ancient settlements usually located next to
deserts | |
mountains | |
oceans | |
rainforests | |
rivers |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (E). Water is necessary for agriculture and human consumption, which eliminates (A), (B), and (D). Ocean water (C) is salty and cannot be consumed by humans. Prior to the invention of irrigation, humans would settle next to rivers, hoping they would flood and cover their crops.
Question 5 |
What was the most populous city in 1800?
London | |
Mumbai | |
New York | |
Rome | |
Shanghai |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Britain industrialized first, and London was the world’s largest city.
Question 6 |
When examining the ten most populous cities in the world, one finds a majority of them in
Africa | |
Asia | |
Europe | |
North America | |
South America |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Almost all the world’s largest cities are in Asia. China and India, which are the two most populous countries in the world, are in Asia.
Question 7 |
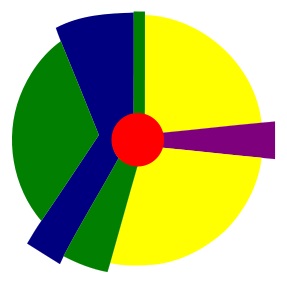
The urban model pictured above is the
Burgess concentric zone model | |
Harris and Ullman multiple nuclei model | |
Hoyt sector model | |
galactic city model | |
gravity model |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). This question requires you to memorize the three models of urban geography. The concentric zone model (A) and multiple-nuclei model (B) are the other two urban models. The two remaining answers are not related to the question.
Question 8 |

The center circle in the model above is the
central business district (CBD) | |
factory and industrial district | |
zone of lower-class housing | |
zone of middle-class housing | |
zone of upper-class housing |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The CBD is at the center of both the sector model and the concentric zone model.
Question 9 |
A city following which of the following models would probably have the lowest density gradient at its core?
Burgess concentric zone model | |
Harris and Ullman multiple nuclei model | |
Hoyt sector model | |
Galactic city model | |
Gravity model |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The galactic city model is the model of the decentralized, post-industrial city. Goods and services are sold primarily outside of the CBD, and residents most likely own an automobile or have access to good mass transit, which lowers the density gradient in the CBD and surrounding area.
Question 10 |
All of the following are true of cities EXCEPT
Latin American cities tend to follow the concentric zone model. | |
Low-income Europeans may live in the suburbs due to the widespread presence of public transportation. | |
Megacities tend to be found in less-developed countries. | |
The sector model tends to be based along transportation corridors. | |
Zoning laws may confine low-income Americans to the inner city. |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Latin American cities follow the sector model.
Question 11 |
When considering modern metropolitan areas, which of the following are “pull” factors to the CBD?
I. Art museums, live theater, and other cultural amenities
II. Counter urbanization
III. Edge cities
IV. Gentrification
I, III | |
I, IV | |
II, IV | |
I, II, III | |
II, III, IV |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B) Counter urbanization is the pull of people away from cities and suburbs and into small towns, so (C), (D), and (E) may be eliminated. An edge city is a business, shopping, and entertainment district built away from the CBD, usually in the suburbs, which eliminates (A), (D), and (E).
People are attracted to art museums, live theater, and other cultural amenities, and gentrification — the process of renovating and improving a house or district so that it conforms to middle-class taste — provides housing in the CBD to people who can afford it.
People are attracted to art museums, live theater, and other cultural amenities, and gentrification — the process of renovating and improving a house or district so that it conforms to middle-class taste — provides housing in the CBD to people who can afford it.
Question 12 |
Racial segregation in American metropolitan areas was caused by all the following EXCEPT
access to public transit | |
blockbusting | |
redlining | |
restrictive covenants | |
zoning laws that required suburban homes to be built on large lots |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Access to public transit reduces segregation. Blockbusting is the practice of persuading owners to sell property cheaply because of the fear of people of another race or class moving into the neighborhood. Redlining is a form of discriminatory lending practices that bar certain groups of people from obtaining mortgage loans. Restrictive covenants were used to bar white people from selling property to African Americans. Zoning laws required lots and homes to be larger than what most African-Americans could afford.
Question 13 |
Which of the following caused rapid suburbanization in the United States after the World War II?
I. Expansion of the interstate highway system
II. Government-subsidized mortgages for veterans
III. Mass production of the automobile
IV. Public housing programs
I, II | |
I, III | |
II, IV | |
I, II, III | |
I, II, III, IV |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Public housing has almost always been built in the inner city. Knowing that fact eliminates answers (C) and (E). All the other Roman numerals are true,
Question 14 |
All of the following encourage counter urbanization EXCEPT
decentralization of public services | |
edge cities | |
gentrification | |
the internet and express package delivery | |
interstate highways |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Counter urbanization is the movement away from cities. Gentrification draws people to the central business district (CBD), so it does not encourage counter urbanization.
Decentralization of public services and edge cities draw people away from the CBD, so those answers are incorrect. The internet and express package delivery allow people to live anywhere they want and have everything they need delivered at their door, rendering it unnecessary to venture to the CBD. Interstate highways make is easier to live in the suburbs and commute to the CBD.
Decentralization of public services and edge cities draw people away from the CBD, so those answers are incorrect. The internet and express package delivery allow people to live anywhere they want and have everything they need delivered at their door, rendering it unnecessary to venture to the CBD. Interstate highways make is easier to live in the suburbs and commute to the CBD.
Question 15 |
A person lives between a small settlement and a settlement that is three times the size of the small settlement. Which of the following is NOT a reason to shop in the larger of the two settlements?
Availability of interstate highways | |
Greater variety of goods and services in the larger settlement | |
Living halfway between the two settlements | |
Living slightly closer to the smaller settlement than to the larger settlement | |
working in the smaller settlement |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (E). Interstate highways would allow a person to get to the larger settlement quickly, so (A) is incorrect. A greater variety of goods and services would draw people to the larger settlement, which means (B) is incorrect. According to the gravity model, a person would have to live very close to the small settlement to be attracted to the small settlement, so (C) and (D) are incorrect. If people work in the small settlement, they would likely shop there on their way home from work, so the answer is (E).
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 15 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Industrial & Economic Development >>
AP Human Geography Main Menu >>
