Unit 2 of AP Human Geography addresses the theories, policies, and causes and effects of the ever-changing distribution of the world’s population. Take our 15-question quiz to review the population and migration concepts pertinent to human geography studies.
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Ancient river valleys, such as the Tigris and Euphrates or the Nile, had comparatively high population densities because of their
arid climates | |
tropical climates | |
natural barriers from attacks by nomads | |
proximity to water | |
proximity to trading partners |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). No civilization can survive without water, which is used for drinking, irrigation, and trade. Arid climates (A) rarely have large numbers of people, and not all river valley civilization meet the other criteria in (B), (C), and (E).
Question 2 |
The United States had a crude birth rate (CBR) of 13.2 in 2013, which means
13.2 babies were born per 100 people | |
13.2 babies were born per 1,000 people | |
132 babies were born per 1,000 people | |
the number of babies born increased by 13.2 percent over the number of babies born in 2012 | |
the number of babies born increased by 1.32 percent over the number of babies born in 2012 |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Birth rates, death rates, and most other demographic characteristics are expressed in thousands.
Question 3 |
One would expect to find a population with a relatively older age structure in
less developed countries | |
more developed countries | |
countries with high death rates | |
countries with high fertility rates | |
countries with low standards of living |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). An older age structure means people are living longer. A high fertility rate (D) indicates a young population. All the other answers indicate people are not living long.
Question 4 |
A country is likely to be in which stage of the demographic transition when its birth rate significantly exceeds its death rate?
Stage 1 | |
Stage 2 | |
Stage 3 | |
Stage 4 | |
Stage 5 |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Stage 1 has high birthrates and high death rates. Stage 2 has high birth rates and declining death rates. In stage 3, both birth rates and death rates decline, and they are both low in stage 4. In stage 5, birth rates are so low that the elderly outnumber the young.
Question 5 |
A country in 2017 with a natural increase rate at or about zero is at which stage of the demographic transition?
Stage 1 | |
Stage 2 | |
Stage 3 | |
Stage 4 | |
Stage 5 |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The natural increase rate equals the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate. It would be about zero in stages 1 and 4, but stage 1 countries no longer exist. Therefore, the correct answer is stage 4.
Question 6 |
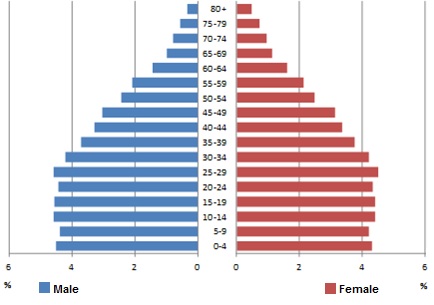
The population pyramid above shows a country at which stage of the demographic transition?
Stage 1 | |
Stage 2 | |
Stage 3 | |
Stage 4 | |
Stage 5 |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The pyramid is halfway between a true pyramid (stage 2) and a rectangle (stage 4).
Question 7 |
A country with a natural increase rate at or about zero is likely to have a
low fertility rate, low standard of living, and few people employed in agriculture | |
low fertility rate, low standard of living, and many people employed in agriculture | |
low fertility rate, high standard of living, and few people employed in agriculture | |
low fertility rate, high standard of living, and many people employed in agriculture | |
high fertility rate, high standard of living, and many people employed in agriculture |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). A lower fertility rate indicates a high standard of living, so (A) and (B) can be eliminated. A high fertility rate indicates a low standard of living, so (E) and can be eliminated. A country with a high standard of living will have access to technology, and therefore, will have relatively few people employed in agriculture, which means (C) is the correct answer.
Question 8 |
Countries at the end of the demographic transition are likely to have problems caring for ____________ but can solve that problem by accepting ____________.
young children, emigrants | |
young children, immigrants | |
elderly, emigrants | |
elderly, immigrants | |
elderly, universal healthcare |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Countries in stages 4 or 5 have declining birthrates, which means the percentage of elderly within the population increases. That fact eliminates (A) and (B). While universal healthcare (E) might be appealing, there would not be enough workers to pay the taxes to support it in a stage 5 country. Countries that accept immigrants (D), however, have enough workers to support the elderly.
Question 9 |
Which of the following is NOT true of the one-child policy?
It decreased China’s birth rate | |
It was still in Chinese law in 2017 | |
It resulted in an imbalanced sex ratio | |
It provided families with incentives to have fewer children | |
Exceptions were made for rural families and some ethnic minorities |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). China’s one-child policy has not existed since 2015. The sex imbalance (C) was caused by the prevalence of sex-selective abortions and female infanticide.
Question 10 |
A country has positive net migration when it has
more immigrants than emigrants | |
more emigrants than immigrants | |
more internal migration than external migration | |
more external migration than external migration | |
more affluent migrants than impoverished migrants |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Emigrants leave a country; immigrants arrive in a country.
Question 11 |
During the first half of the nineteenth century, migration in the United States went from
east to west | |
north to south | |
south to north | |
rural areas to urban areas | |
urban areas to rural areas |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A) This is known as the westward expansion. Answer (B) describes the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries. Answer (C) is a reference to the Great Migration. Answer (D) describes the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Answer (E) is counter urbanization, a recent phenomenon.
Question 12 |
U.S. quota laws from the 1920s until the 1960s
greatly expanded migration | |
limited migration to refugees | |
limited racial diversity | |
prohibited migration from Asia | |
reversed a demographic decline |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). U.S. quota laws limited the number of immigrants based on the percentage of the population already living in the United States. Since most Americans were descended from Europeans, these quota laws kept the United States overwhelming white.
Question 13 |
Individuals with special talents may be exempt from quota laws. When the United States makes exceptions for those people, it is accused of
brain drain | |
chain migration | |
discrimination | |
exclusion | |
racism |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Brain drain occurs when large numbers of educated and very skilled people leave their own country to live and work in another country where pay and/or conditions are better. Although some people might accuse the United States of discrimination, exclusion, and racism, none of these answers are correct for this question. Chain migration is the process by which immigrants settle in areas already settled by friends and relatives.
Question 14 |
Which of the following describe the characteristics of most immigrants today?
I. Young
II. Old
III. Married
IV. Single
V. Living in a country in the early stages of the demographic transition
VI. Living in a country in the later stages of the demographic transition
II, III | |
I, III, V | |
I, III, VI | |
I, IV, V | |
I, IV, VI |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (E). People who are young and single are more likely to move because they are not tied to their homelands. Therefore, (A), (B), and (C) may be eliminated. Answer (D) is wrong because immigrants have already moved, and they move to places that are further along in the demographic transition.
Question 15 |
Which of the following are push factors in migration?
Desire to attend college out of state, natural disasters, new employment opportunities | |
Desire to attend college out of state, friends and relatives living in another country, unemployment | |
Desire to attend college out of state, friends and relatives living in another country, new employment opportunities | |
Natural disasters, new employment opportunities, war | |
Natural disasters, unemployment, war |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (E). Push factors are undesirable things that force people to move. Only answer (E) has three push factors. Answer (C) is made up of three pull factors, which involve voluntary migration. Answers (A), (B), and (D) are a mix of push and pull factors.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 15 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Cultural Patterns & Processes >>
AP Human Geography Main Menu >>
