Our free AP Environmental Science unit 4 practice test covers Earth systems and resources. Earth systems such as plate tectonics, global wind distribution, soil formation, and solar energy play a pivotal role in the ability of life to thrive on our planet.
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
An area beneath the ocean floor where tectonic plates move away from each other is known as a:
Subduction zone | |
Divergent plate boundary | |
Convergent plate boundary | |
Transform fault boundary |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Beneath the ocean floor, tectonic plates move away from each other at the divergent plate boundary. A subduction zone is where the tectonic plates pass over one another. Seafloor spreading does not describe the movement of the plates; instead, it describes the mantle pushing upward through to the surface. At a convergent plate boundary, the tectonic plates move toward one another, and at a transform fault boundary, the plates move past each other. The tectonic plates move away from each other due to the force of magma rising through and splitting the lithosphere, of which the tectonic plates are made.
Question 2 |
Which of the following layers of the earth is entirely liquid?
Inner core | |
Outer core | |
Mantle | |
Lithosphere |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The inner and outer core of the earth both consist of iron and nickel. Although the inner core is hot, its accompanying 330–360 gigapascal pressure keeps it in the solid phase. The outer core, although hot, lacks the pressure to keep it in the solid phase; consequently, it is the only layer of Earth in the liquid phase. The mantle is made up of magma, which is molten rock and not considered liquid. The asthenosphere is semi-molten but not liquid. The lithosphere is composed of both the earth’s crust and the outer mantle, both of which are solid.
Question 3 |
The loss of some or all of a soil’s ability to support plant growth is called
Erosion | |
Soil degradation | |
Physical weathering | |
Chemical weathering |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Soil degradation describes the loss of some or all of a soil’s ability to support plant growth resulting from biological, chemical, or physical deterioration. Weathering describes the breakdown of rocks and minerals, not soil. Erosion describes the process by which rock fragments and soils are removed from a landscape, but it does not specifically describe a soil’s capacity for supporting plant growth. Base saturation describes the proportion of soil bases to soil acids and does not specifically relate to soil-supported plant growth.
Question 4 |
Which list orders soil types from least to most organic content?
Young soil, immature soil, mature soil | |
Immature soil, young soil, mature soil | |
Mature soil, immature soil, young soil | |
Mature soil, young soil, immature soil |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). As soil ages, the amount of organic material in it increases proportionally. Immature soil develops into young soil as plants and organisms die. Eventually, young soil becomes mature soil, which contains all of the organic material present in each of the earlier stages.
Question 5 |
Which list shows the layers of the atmosphere in order, starting with the layer closest to earth?
Stratosphere, troposphere, mesosphere, thermosphere | |
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere | |
Stratosphere, troposphere, thermosphere, mesosphere | |
Troposphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The troposphere is the lowest portion of the atmosphere and ranges in depth from about 8 km – 14.5 km. The stratosphere is the second layer of the atmosphere and contains the ozone layer. The third layer, the mesosphere, is where most meteors burn up when entering the atmosphere. The thermosphere is the fourth layer and is where the International Space Station orbits.
Question 6 |
Which of the following correctly lists the layers of the earth from the innermost layer to the outside layer?
Solid inner core, liquid outer core, mantle, crust | |
Liquid outer core, solid inner core, mantle, crust | |
Solid inner core, liquid outer core, crust, mantle | |
Crust, mantle, liquid outer core, solid inner core |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The innermost layer of the earth is the solid inner core, followed by the liquid outer core, the mantle, and finally the crust.
Question 7 |
Which type of plate interaction occurs when plates move sideways past each other?
Fault zone | |
Divergent plate boundary | |
Convergent plate boundary | |
Transform plate boundary |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Transform plate boundaries occur when plates move sideways past each other.
Question 8 |
Which soil horizon is composed mainly of mineral material with very little organic matter?
O horizon | |
A horizon | |
B horizon | |
D horizon |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The B horizon consists mostly of minerals and very little organic matter.
Question 9 |
The percentages of the soil’s sand, silt, and clay is referred to as:
Texture | |
Minerals | |
Horizons | |
Relative particle size |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). A soil’s texture is determined by the percentages of sand, silt, and clay contained in the soil.
Question 10 |
Where is the greatest amount of fresh water located on Earth?
Water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and ponds | |
The atmosphere | |
Oceans | |
Ice and glaciers |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). No more than 3% of Earth’s water is fresh water. Fresh water sources are approximately distributed as follows:
0.04% atmospheric water
0.3% surface water
30% ground water
68+% ice and glaciers
0.04% atmospheric water
0.3% surface water
30% ground water
68+% ice and glaciers
Question 11 |
Which of the following atmospheric layers is the closest to the earth?
Thermosphere | |
Troposphere | |
Mesosphere | |
Stratosphere |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The following lists the atmospheric layer from the closest to the Earth increasing in altitude:
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Exosphere
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Exosphere
Question 12 |
What could a farmer do to prevent crop loss due to heavy rains waterlogging his crops?
The farmer could amend his soil with clay to decrease porosity | |
The farmer could use contour plowing to prevent soil erosion | |
The farmer could use cover crops to increase organic material in the soil | |
The farmer could amend his soil with sand to increase porosity |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Amending the soil with sand would increase the porosity of the soil, allowing water to drain better and decreasing the chance of crops drowning. Clay would cause the water to sit on the surface even longer due to decreased porosity. Contour plowing would likewise help the water to sit in place longer. Increased organic material in soil also increases water-holding capacity.
Question 13 |
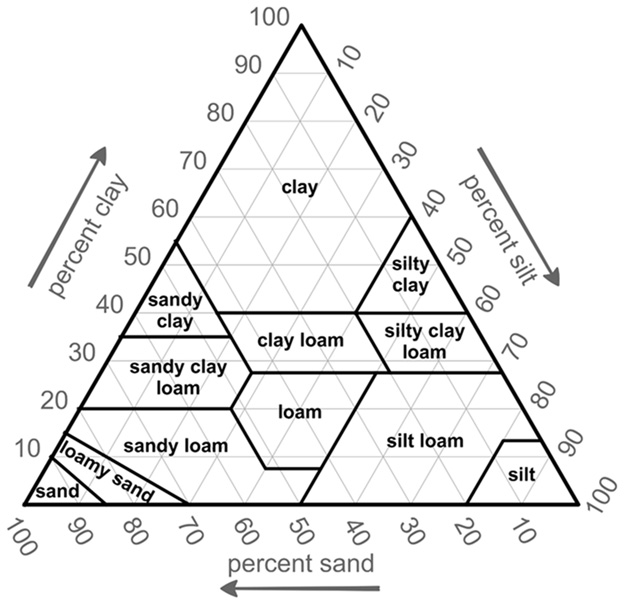
In the image above, which category would soil fall into if it is 30% sand, 10% clay, and 60% silt?
Silty clay | |
Loam | |
Silt Loam | |
Sandy Loam |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). To read the above chart, start with the percent sand and find the intersecting line with clay and then silt.
Question 14 |
Which layer of the Earth’s atmosphere contains the highest percentage of water vapor?
The troposphere | |
The stratosphere | |
The mesosphere | |
The thermosphere |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Most weather occurs in the troposphere, where water evaporating from the surface of the Earth rises with warm air; as the air cools, the water condenses and falls back to the surface as precipitation.
Question 15 |
Which is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume?
CO2 | |
CH4 | |
O2 | |
N2 |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). 78% of our atmosphere is Nitrogen. Oxygen makes up 21%, and the rest of the gases account for around 1% by volume.
Question 16 |
Soybeans require soil that drains well to grow well. Which type of soil would be best to farm soybeans in?
Soil that contains at least 45% clay so that it retains plenty of water | |
Soil that contains at least 80% silt due to its low amounts of sand | |
Sandy loam that contains less than 20% clay | |
Silty clay loam because it contains all three soil components |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Clay has the lowest porosity of the three components of soil and prevents drainage. Sandy loam has higher amounts of sand and silt, allowing good drainage while still holding enough water for the soybeans.
Question 17 |
Which of the following has the greatest effect on the global distribution of solar energy that leads to seasons?
The tilt of the Earth’s axis concerning the sun | |
The curvature of the Earth | |
The shape of the Earth's orbit | |
The location of the Earth’s landmasses |
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The tilt of the Earth’s axis is what drives the Earth’s seasons, as the hemisphere tilted towards the sun receives more solar energy than the hemisphere tilted away from the sun.
Question 18 |
Which agricultural practice would most likely lead to lower turbidity in nearby rivers and streams?
Using crop rotation in fields | |
Removing excess vegetation surrounding crop fields | |
Using synthetic fertilizers | |
Changing fields from crops to cattle pasture |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Crop rotation helps to reduce soil erosion. Increased soil erosion leads to more sediment in local waterways. Removing vegetation around the fields would also increase soil erosion, as would turning fields into cattle pasture. Use of synthetic fertilizers can lead to eutrophication in local waterways if excess N and P runoff from the fields makes its way into them.
Question 19 |
Though Iceland and Greenland are found at similar latitudes in the North Atlantic Ocean, Iceland sees a considerably warmer average daily temperature year round and is not covered by glaciers the way that Greenland is. Which of the following best explains the difference in the climates of Greenland and Iceland?
Solar radiation reaching Greenland is of higher intensity, leading it to more readily reflect off of the glaciers found there | |
Oceanic currents from equatorial regions flow around the coast of Iceland, helping to warm the atmosphere | |
The people living in Iceland have altered the climate to be more suitable | |
Polar air currents move at greater speeds over Greenland, stripping away much of the heat there |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Warm water currents flow up and around Iceland as part of thermohaline circulation. Cold arctic currents then flow down and around Greenland, having the opposite effect. Both countries receive a similar amount and intensity of solar radiation.
Question 20 |
Dams are built to regulate flooding downstream and occasionally to produce hydroelectric power. Which of the following is a negative environmental impact of building a dam on a river?
Sediment is prevented from flowing downstream, which can lower the productivity of portions of the river past the dam as well as any wetlands found at the mouth of the river | |
A new habitat will form behind the dam that can increase recreational spending in the area | |
More regulated flow downstream will stabilize the banks of the river | |
Local human populations will benefit from the increase in green, renewable energy |
Question 20 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Sediment carried downstream by rivers brings needed nutrients to the ecosystems found there.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 20 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Unit 5: Land & Water Use >>
AP Environmental Science Main Menu >>
