Our free AP Environmental Science unit 2 practice test covers biodiversity. In this unit, students learn about the different levels of biodiversity and why biodiversity is so important to a healthy environment.
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which of the following tree species is a pioneer species in North American forests?
Beech | |
Aspen | |
Maple | |
Oak |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). A pioneer species is a species of tree that can colonize new areas quickly and thrive. The aspen tree is often referred to as a pioneer species because of its ability to colonize new environments rapidly and maintain its longevity regardless of potential fires.
Question 2 |
Which of the following is the measurement used by ecologists to determine the biodiversity of a particular area?
Species richness | |
Species evenness | |
Genetic diversity | |
Ecosystem diversity |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The number of species in a given area, such as a grassland, is known as species richness.
Question 3 |
Which evolutionary process takes place when disturbance causes a dramatic decrease in the population size, causing the genetic composition of the survivors to substantially differ from the original group?
Mutation | |
Genetic drift | |
Founder effect | |
Bottleneck effect |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). If a population is drastically reduced, the genetic composition may change. For example, if a natural disaster reduced the population to a small size, there will be fewer unique genotypes present in the remaining population. The offspring of these individuals will not be as genetically diverse due to the limited alleles present.
Question 4 |
At which level of complexity does evolution occur?
Ecosystem | |
Community | |
Population | |
Species |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). A population is a group of individuals of the same species. Evolution requires genetic variation. Population is the lowest level of the organization of life at which such variation exists.
Question 5 |
Which of the following factors does not influence species richness of a community?
Habitat size | |
Distance from other communities | |
The length of time the habitat has existed | |
The amount of biomass |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Latitude influences the species richness—the further organisms are away from the North or South Pole, the species richness increases. The size of the habitat and the distance of that habitat from a source of colonizing species influence species richness as well. Species richness is also influenced by the length of time the habitat has existed, in that the longer the habitat has existed, the greater the species richness. However, amount of biomass in an ecosystem does not influence species richness.
Question 6 |
Organisms need to acquire energy to survive. Which of the following are examples of adaptations that allow organisms to acquire the energy needed?
I. The long, slender beak of a hummingbird
II. The echolocation of a dolphin
III. The eyesight of an eagle
I only | |
II only | |
I and III | |
I, II, and III |
Question 6 Explanation:
All three choices are correct, so the correct answer is (D). The beak allows the hummingbird to reach nectar in deep flowers. The echolocation allows the dolphin to locate fish in murky water. The eyesight allows the eagle to spot food from far away.
Question 7 |
Which of the following would be a cultural service of an ecosystem?
Timber produced by trees | |
Food items like nuts and berries | |
Hiking paths to enjoy nature | |
Air purification by native plants |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Cultural ecosystem services are the benefits people gain from their interactions with different environmental spaces, such as woods or parks, and the activities, such as walking and cycling, they undertake in these spaces. The other three answer choices would be economic services provided by an ecosystem as they all have financial benefits for the people living near them.
Question 8 |
The finches from the Galapagos islands are descended from one ancestral species that arrived millions of years ago. The primary difference between the species there now consists of different-sized and shaped beaks to use different food sources on the island.
Which of the following best describes why the ancestral finch species evolved into several distinct species after arriving on the islands?
Limited resources in the island ecosystems led to the adaptation of specialist traits to reduce competition between members of the species | |
An abundance of resources on the islands allowed the ancestral finches to be successful in filling all available niches | |
Reduced competition from other bird species allowed the finches to adapt to different food sources | |
Island climates tend to be more stable, which allowed the finches a consistent food source from year to year |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Islands tend to have fewer resources due to their smaller size and isolation from other sources of biodiversity. This lack of resources leads to adaptive radiation as a way to reduce competition and make use of the unoccupied niches.
Question 9 |
According to the theory of island biogeography, which two characteristics of islands should determine the levels of biodiversity found on them?
Size and soil type | |
Distance to the nearest source of biodiversity and the number of islands in the area | |
Number of islands in the area and soil type | |
Size and distance to the nearest source of biodiversity |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The size of an island determines the possible population size of species found there, the number of different ecosystems found there, and the types of species that can be found there. The distance to the nearest source of biodiversity determines how easily new species can make their way to the island. Less isolated islands see greater levels of immigration.
Question 10 |
Which of the following is a likely impact of the slash-and-burn style removal of the Amazon rainforest?
Increased CFCs reducing atmospheric ozone | |
Increased carbon sequestration | |
Decreased soil erosion compared to traditional logging | |
Increased average global temperatures due to higher atmospheric CO2 |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Slash and burn puts the majority of the CO2 sequestered in the trees immediately into the atmosphere as well as removing the ability of the trees to continue sequestering more CO2 . Increased atmospheric CO2 leads to warmer global temperatures because it is a greenhouse gas that traps heat radiated from the surface of the Earth.
Question 11 |
Giant tube worms live on the ocean floor near hydrothermal vents. This environment experiences temperatures far hotter than most organisms can withstand and contains a high concentration of toxic chemicals such as hydrogen sulfide that escape from the vents. Which of the following statements best explains why the giant tube worm can survive in this environment?
Competitors of the giant tube worm were wiped out by pollution, allowing the worms to dominate the ecosystem | |
The toxic environment near the vents led to a trophic cascade that eliminated tube worm predators | |
Giant tube worms are well adapted to the environment near the vents and can thrive there outside the range of tolerance of other organisms | |
Giant tube worms can survive in any environment, so it makes sense that they would fill an available niche |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Giant tube worms have special adaptations that allow them to survive near-boiling water and use the bacteria that feed on hydrogen sulfide as food source.
Question 12 |
Based on the theory of island biogeography, why would a scientist expect to find less biodiversity on an island 25 kilometers from the mainland than on an island 8 kilometers from the mainland?
More species have the ability to travel to an island 8 kilometers away than to one 25 kilometers away | |
Islands closer to the mainland always have greater ecosystem diversity than islands further from the mainland | |
Islands further from the mainland normally have fewer available niches | |
Islands further from the mainland tend to see increased immigration as compared to islands closer to the mainland |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). More organisms would have the ability to travel the shorter distance between the closer island and the mainland.
Question 13 |
A local ecologist has noticed that the population of bald eagles has fallen considerably over the past several years while other populations have remained stable. After running tests, the ecologist found that levels of DDT in fish in the area were extremely high. In this case, the bald eagles would be considered:
Pioneer species | |
Primary consumer | |
R-selected species | |
Indicator species |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The decrease in the bald eagle population served as an initial indication that something was wrong in the ecosystem. This led the ecologist to look for answers.
Question 14 |
Urban barn swallows have adapted to live under the bridges of busy expressways in major metropolitan areas. Below is a group of measurements of wing length from a population of barn swallows living under bridges and a population of barn swallows living in a rural setting.
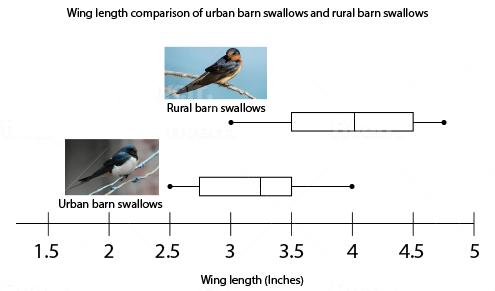
Which of the following can explain the difference in wing length seen between the two populations?
Rural barn swallows need longer wings to better navigate the more natural ecosystem they are found in | |
Urban barn swallows need shorter wings to better avoid the fast-moving traffic under the bridges, whereas longer wings would make them less maneuverable and more likely to be struck by cars | |
Rural barn swallows have accumulated a different set of random mutations that led to longer wings | |
Urban barn swallows do not live long enough to grow to the larger-sized wings of the rural barn swallows |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The smaller wings of the urban swallows permit better maneuverability to evade traffic so that, over several generations, the swallows with shorter wings had a greater rate of survival. As a result, the population gradually had shorter and shorter average wing length.
Question 15 |
Which of the following is the best example of a keystone species in a pond ecosystem?
Bluegill | |
Stork | |
Dragonfly | |
Beaver |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Beavers help to create ponds by building dams in streams and creeks. The other species would then inhabit the ecosystem created by the beaver.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 15 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Unit 3: Populations >>
AP Environmental Science Main Menu >>
