Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Yeast and mammals share very similar cell communication molecules and pathways. What does this suggest about yeast and mammals?
Yeast and mammals share a recent common ancestor | |
Early versions of cell communication mechanisms still used today must have evolved before the first multicellular organisms | |
Signaling molecules first evolved in multicellular eukaryotes | |
All cell communication systems are used for sexual reproduction |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Even though the last common ancestor of yeast and mammals lived over a billion years ago, the molecular details of signal transduction in yeast and mammals is very similar.
Question 2 |
Which of the following is an example of long-distance cell signaling?
Cell-cell recognition in animal cells | |
Synaptic signaling in the nervous system | |
Hormonal signaling in humans | |
Plasmodesmata in plant cells |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Cell-cell recognition involves direct contact between cells. Synaptic signaling requires the nerve cell to be very close to the target cell. Plasmodesmata in plant cells is a junction that allows molecules to pass between adjacent cells with out having to cross the plasma membrane. Hormones are used by plants and animals for long-distance signaling.
Question 3 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 3–5
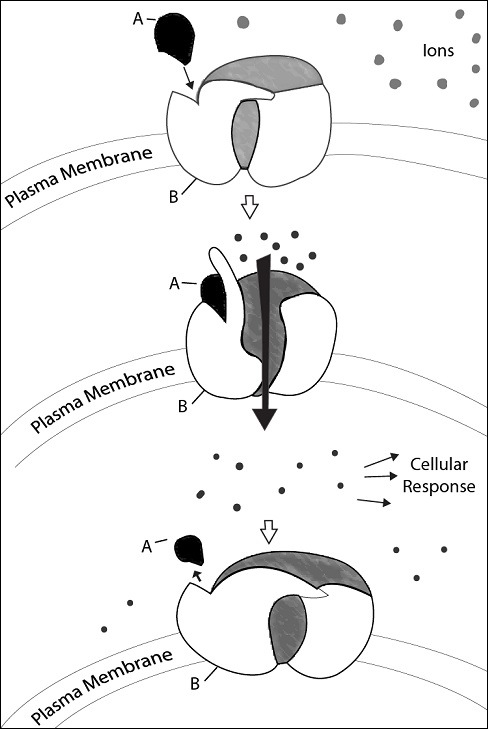
Which type of membrane receptor (B) is represented in the diagram?
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase | |
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel Receptor | |
G Protein-Coupled Receptor | |
Phosphorylation Cascade |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The diagram shows a ligand-gated ion channel receptor with a region that acts as a gate when the receptor changes shape. When the signaling molecule (A) binds to the receptor protein (B), the gate opens and allows ions to flow through to the plasma membrane through the channel receptor.
Question 4 |

What is Part 2 of the diagram showing?
The channel receptor with a closed gate waiting for the signaling molecule to bind to the receptor | |
The dissociation of the receptor from the receptor protein, allowing the gate to close and prohibiting ions from entering | |
The signaling molecule binding to the receptor, allowing the gate to open for ions to flow through the channel | |
A hormone passing through the plasma membrane via a G protein-coupled receptor |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Part 2 the diagram is depicting the action of the signaling molecule binding to the receptor and allowing the gate to open. Specific ions then flow through the channel into the cell.
Question 5 |

What type of molecule is represented by A in the diagram?
Hormone | |
Signaling molecule | |
Receptor protein | |
Active protein |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Signaling molecules are molecules that have a specific shape to “fit” in a portion of the receptor protein, like a key fitting into a lock. The signaling molecule causes the receptor protein to change its shape that directly activates the receptor.
Question 6 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 6–7. The diagram shows two yeast cells (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) using cell communication for a biological process.
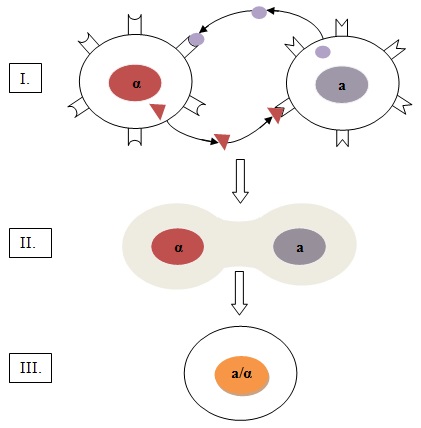
What is illustrated in Part I?
Cells of type a secrete a signaling factor called a which can bind to nearby receptors on α cells | |
Cells of type α use phagocytosis to absorb molecules called a | |
Cells of type a and α are communicating within a multicellular organism to bring about a cellular change | |
Two single celled prokaryotic cells are undergoing asexual reproduction |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Part I shows type a cell secreting factor a which binds to a receptor site on type α cell. Inversely, type α cell is secreting factor α which binds to a receptor site on type a cell.
Question 7 |

What biological process is taking place in the diagram?
Fermentation | |
Budding | |
Signal transduction pathway | |
Zygote formation |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The binding of the factors to the receptors leads to the fusion of the two cells. The nucleus of the fused cell, a zygote, includes all the genetic information from type a cell and type α cell. This zygote can then undergo mitosis leading to the formation of a diploid bud.
Question 8 |
Identify the correct sequence of cell signaling.
Activation of cellular response, Reception, Transduction | |
Transduction, Reception, Activation of cellular response | |
Reception, Transduction, Activation of cellular response | |
Reception, Activation of cellular response, Transduction |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Reception occurs first, when the target cell detects a signaling molecule coming from outside the cell. Next, transduction takes place with the binding of the signaling molecule changing the shape of the receptor protein and initiating the process of transduction. Transduction converts the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response. Finally, the activation of cellular response takes place when the transduced signal triggers a specific cellular response.
Question 9 |
Which part of your nervous system would likely be activated if you just realized you overslept and a final exam begins in just 10 minutes?
Sympathetic | |
Parasympathetic | |
Enteric | |
Reticular |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The sympathetic division gives the “fight-or-flight” response. The parasympathetic division gives the “rest and digest” response. The enteric division consists of networks of neurons in the digestive tract, pancreas and gallbladder. The reticular formation is a network of neurons located at the core of the brainstem, acting as a sensory filter for the cerebral cortex.
Question 10 |
Which of the following choices represents the correct flow of sensory information in a simple sensory pathway?
Reception → Transduction → Transmission → Perception | |
Perception → Transduction → Transmission → Reception | |
Transduction → Transmission → Perception → Reception | |
Reception → Perception → Transmission → Transduction |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Sensory pathways begin with the reception of sensory information, in which the stimulus is detected by sensory cells. The stimulus is converted to a change in the membrane potential of a sensory receptor during transduction. Nerve impulses transmit the sensory information through the nervous system via nerve impulses during transmission. Finally, when the brain receives the information, the information is processed, generating a perception.
Question 11 |
Questions 11–13: Use the diagram below to identify the activity or object in the pathway.
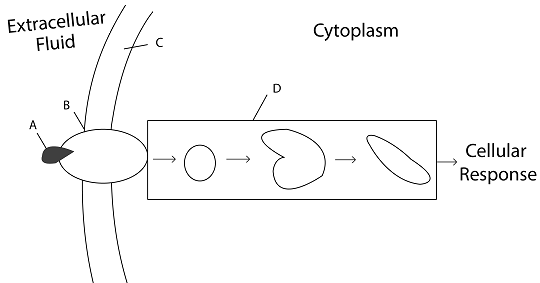
Which letter represents the plasma membrane of the cell?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The plasma membrane is the selectively permeable layer of molecules that encloses the cell.
Question 12 |

Which letter represents a signaling molecule coming from outside the cell?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The receptor protein detects the signaling molecule when the signaling molecule fits into the receptor. This is known as “reception.”
Question 13 |

Which letter represents the conversion of the signal to a form that brings about a cellular response?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Signal transduction pathways are a sequence of changes in a series of molecules, that allows information to trigger a cellular response.
Question 14 |
The cell’s breakdown of sugar generates chemical energy in the form of ATP. When the cell makes more ATP than it can use, the excess ATP inhibits an enzyme near the beginning of the pathway and slows process of ATP production. What type of mechanism is described?
Positive feedback | |
Negative feedback | |
Cell-to-cell signaling | |
Signal recognition pathway |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). A negative feedback system acts to dampen the initial affect whereas a positive feedback system acts to amplify the initial affect.
Question 15 |
During which process do cells enter into programmed cell death, during which time DNA is chopped up, organelles are fragmented, the cell shrinks and parts of the cell are packaged into vesicle and removed by scavenger cells?
Apoptosis | |
Catastrophism | |
Cytokinesis | |
Endocytosis |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Aptosis is controlled suicide of the cell. Catastrophism is the idea that events in the past occurred suddenly and were caused by different mechanisms than those operating today. Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm to form daughter cells after mitosis. Endocytosis is process by which materials enter the cell via the formation of vesicles.
Question 16 |
Which is the correct sequence of mitosis?
Metaphase → Prophase → Anaphase → Telophase → Prometaphase | |
Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase | |
Prometaphase → Metaphase → Prophase → Anaphase → Telophase | |
Telophase → Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The cell cycle progresses through phases of the cell cycle in the following order:
Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase
Prophase → Prometaphase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase
Question 17 |
If a cell has 6 chromosomes in metaphase, how many chromatids would it have?
6 | |
3 | |
12 | |
None |
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Each duplicated chromosome has two sister chromatids. Therefore, 6 chromosomes would include 12 chromatids.
Question 18 |
If a zygote went through a series of 4 cell divisions, how many cells would be in the embryo?
32 | |
10 | |
16 | |
8 |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Each time a cell divides, it become two cells. To calculate the number of cells, square the number of cell divisions; 42 = 16.
Question 19 |
Questions 19–20
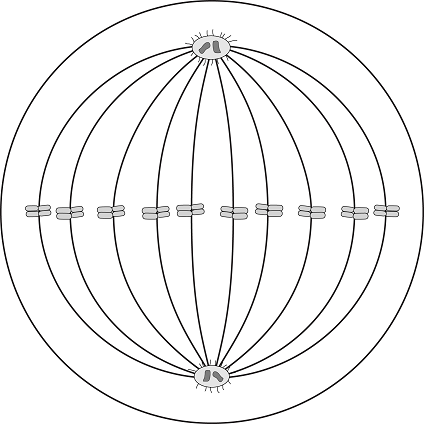
What phase of the cell cycle is represented by the diagram?
Metaphase | |
Prophase | |
Interphase | |
Cytokinesis |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). During metaphase, the chromosomes are lined up along the metaphase plate, the centrosomes are at opposite poles, the kinetochores of the sister chromatids are attached to microtubules coming from opposite poles.
Question 20 |

Swamp wallabies have 10 chromosomes during this phase. How many chromosomes did the wallaby inherit from each parent?
10 | |
5 | |
20 | |
15 |
Question 20 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Somatic cells, like the one pictured here in metaphase, are diploid. If the diploid number is 10, then the organism inherited 5 chromosomes from each parent (the haploid number).
Question 21 |
Which of the following does not produce genetic variation in sexual life cycles?
Crossing over | |
Binary fission | |
Independent assortment of chromosomes | |
Random fertilization |
Question 21 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Binary fission is the type of asexual reproduction used by single-celled eukaryotes, such as amoebas, and prokaryotes.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 21 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Heredity >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
