Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which of the following is not an example of a catabolic pathway?
Glycolysis | |
Cellular respiration | |
Citric Acid Cycle | |
Photosynthesis |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Answers (A), (B) & (C) are catabolic because they result in the net release of energy with the end products being simpler than the input. Photosynthesis is an anabolic pathway since it results in the net gain of energy with the end products of the reaction being more complex than the input.
Question 2 |
A battery being used in a flashlight is an example of:
Rotational Energy | |
Thermal Energy | |
Chemical Energy | |
Solar Energy |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Chemical energy is energy that is stored in chemicals. In the case of the battery, when the positive and negative terminals are connected so that electricity can flow between them, chemical reactions occur at the electrodes. The reactions release excess electrons at the anode which flow to the cathode.
Question 3 |
Which statement is true of a cell in chemical equilibrium?
Cells in chemical equilibrium can no longer do work, and therefore, will die | |
Cells are most stable in chemical equilibrium, and able to produce molecules needed for biological processes to continue | |
Cells in chemical equilibrium are healthy and productive; cells in chemical disequilibrium typically are cancerous | |
As cells reach chemical equilibrium, the free energy of the mixture of reactants and products increases |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). If chemical reactions occurred in a test tube, they would eventually reach chemical equilibrium. Systems with chemical equilibrium have a minimum amount of free energy, and therefore they cannot do any work, and will eventually die. This is a very important aspect of life: that metabolism as a whole is never at equilibrium.
Question 4 |
The pumping of substances across a membrane against the direction of spontaneous movement is which type of work?
Diffusion | |
Active Transport | |
Dialysis | |
Filtration |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Active transport involves the use of transport proteins to move solutes against a concentration gradient, which means they are pumping something (typically ions) from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.
Question 5 |
How do enzymes change the speed of chemical reactions in cells?
They increase the heat in the cell, and therefore speed up the reaction by allowing reactants to attain the transition state more often | |
Enzymes speed up reactions by changing the amount of free energy available in the cell for reactions | |
Enzymes make endergonic reactions exergonic | |
Enzymes speed up reactions by bringing substrates together to undergo a chemical reaction |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Enzymes have a specialized area on the molecules called the active site, which bring substrates together for a chemical reaction to take place.
Question 6 |
Which of the following environmental conditions does not affect the activity of enzymes?
Temperatures | |
The amount of free energy in the cell | |
pH | |
Chemicals in the enzyme’s environment |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Typically, the rate of enzymatic reactions increases with temperature (up to a point), this is because increased temperature means increased energy means increased motion which makes for more frequent collisions of substrates with active sites. pH can have an impact on the functioning of an enzyme. For example, the stomach enzyme pepsin works best at a pH of about 1.5 and the enzyme trypsin, which acts in the small intestine, works best at a pH of about 8. Because enzymes are sensitive to their environment, certain chemicals can denature the protein, rendering it unable to perform its function. The amount of free energy in the cell does not affect the function of the enzyme.
Question 7 |
Questions 7–8
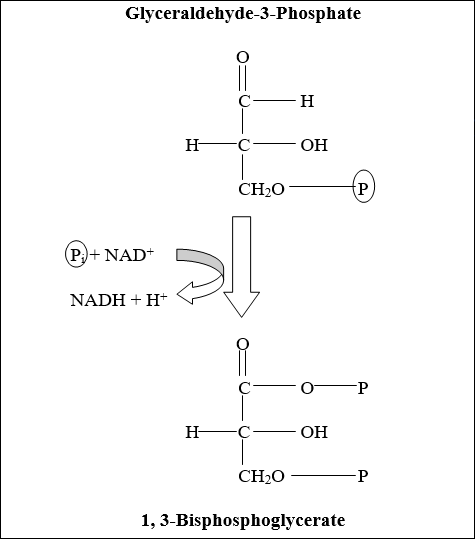
During the above reaction in glycolysis, which molecule acts as the oxidizing agent?
NAD+ | |
NADH | |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate | |
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). NAD+ is the oxidizing agent because it accepts electrons from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
Question 8 |
Questions 7–8

In the same reaction above in glycolysis, which molecule acts as the reducing agent?
NAD+ | |
NADH | |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate | |
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is the reducing agent because it donates electrons to NAD+.
Question 9 |
Which of the following biological process is not a step in cellular respiration:
Citric Acid Cycle | |
Oxidative Phosphorylation | |
Glycolysis | |
Calvin Cycle |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The Calvin Cycle is a the process by which ATP and NADPH convert CO2 to sugar in photosynthesis.
Question 10 |
During which phase of cellular respiration is the most ATP produced?
Glycolysis | |
Oxidative Phosphorylation | |
Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA | |
Citric Acid Cycle |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Oxidative phosphorylation uses energy released by the electron transport chain to power ATP synthesis.
Question 11 |
Which metabolic pathway is used by cellular respiration and fermentation?
Glycolysis | |
Citric Acid Cycle | |
Electron Transport Chain | |
Oxidative Phosphorylation |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Fermentation consists of glycolysis plus reactions that regenerate NAD+.
Question 12 |
Which part of photosynthesis takes place in the stroma, uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to the sugar G3P, and returns ADP and NADP+?
Calvin Cycle | |
Light Reactions | |
Chemiosmosis | |
Electron Transport Chain |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The Calvin Cycle can be broken down into 3 steps: (1) Carbon fixation, which incorporates each CO2 molecule by attaching it to a 5-carbon sugar (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate), (2) Reduction, where each molecule of 3-phosphoglycerate receives an additional phosphate group from ATP and hydrogen from NADPH forming glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, and (3) Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate). This all takes place in the stroma.
Question 13 |
Which of the following reactions represents photosynthesis?
Pyruvate + NADH + H+ → Lactate + NAD2 | |
C4H6O5 + NAD+ → C4H4O5 + NADH + H+ | |
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy | |
6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The summary equation of photosynthesis is the reverse of that of cellular respiration. Carbon dioxide, plus water, plus energy in the form of light are converted to glucose and oxygen inside a chloroplast.
Question 14 |
What color of light is least effective in driving photosynthesis?
Red | |
Yellow | |
Green | |
Orange |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Most plants appear to be green. This is because green light is reflected and not available to provide energy for photosynthesis.
Question 15 |
Which type of plants has a unique leaf structure, specifically adapted to hot, dry climates which helps to maintain CO2 concentration in the bundle sheath that favors photosynthesis over photorespiration?
C4 Plants | |
C3 Plants | |
CAM Plants | |
Parasitic Plants |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). C4 plants are given such a name because they preface the Calvin Cycle with an alternate mode of carbon fixation that forms a 4-carbon compound as its first product.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 15 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Internal Environments >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
