Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
The relationship between cleaner fish and the fish they clean is best described as:
Predation | |
Competition | |
Mutualism | |
Commensalism |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Mutualism describes a relationship in which both interacting members benefit. In this example, the cleaner fish feed on the parasites that are on their clients and their clients are healthier for having the parasites removed.
Question 2 |
Which type of chemical bond involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in oppositely charged ions that are attracted to each other?
Covalent bond | |
Ionic bond | |
Hydrogen bond | |
Van der Waals interactions |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, causing the atoms to have opposite charges and attract each other. Hydrogen bonds result from the attraction between partial positive and negative charges in atoms. Van der Waals interactions are weak attractions that occur when atoms and molecules are very close together.
Question 3 |
Which property of water allows it to move upward from the roots of a tree to its leaves?
High specific heat | |
High heat of vaporization | |
Cohesion | |
Solvent of life |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). As water evaporates from the leaves of trees, the property of cohesion (attraction to another water molecule) allows the water molecules leaving the plant to pull molecules upward because they are attracted though hydrogen bonds.
Question 4 |
Use the diagram below to answer question 4:
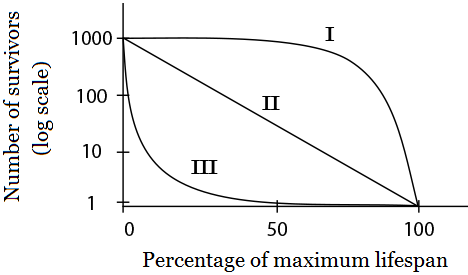
A sea turtle lays approximately 100 eggs at a time, yet on average only one of the eggs will survive to adulthood. Which type of survivorship curve represents a sea turtle population?
Type I | |
Type II | |
Type III | |
Types II and III |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Organisms with Type III survivorship curves experience high early mortality.
Question 5 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 5–7:
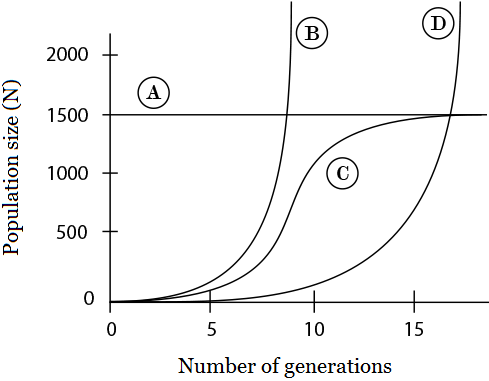
Which line represents a population of organisms with a highest maximum growth rate increase?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Line B grows exponentially faster than the other lines.
Question 6 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 5–7:

Which line represents a population’s carrying capacity (K)?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Carrying capacity represents the maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain.
Question 7 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 5–7:

What does Line C represent?
Exponential growth | |
Zero population growth | |
Geometric population growth | |
Logistic population growth |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Logistic population growth model indicates that population growth increase will reach zero as the population reaches carrying capacity.
Question 8 |
Which of the following environmental issues has the most impact on the distribution of local and global ecosystems over time?
Global warming | |
Biodiversity | |
Acid rain | |
Habitat fragmentation |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The most important factor limiting the geographic range for plants and animals is climate. Global warming shifts the climate around the globe, and thus will influence the distribution of ecosystems.
Question 9 |
Some enzymes require an effector in order to conform to a substrate. The site to which the effector binds is the:
Active site | |
Affective site | |
Allosteric site | |
Effector site |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The binding of an effector to the allosteric site will change the shape of the active site (the site to which the substrate binds) allowing (or preventing) the substrate to attach.
Question 10 |
The loss of a predator population from a community can lead to an explosion of prey populations, allowing for intense competition between these species for resources. The result will be a drastic change in community structure. What name is given to a species that plays such a key role in maintaining community structure?
Dominant species | |
Apex species | |
Top species | |
Keystone species |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Keystone species play a major role in maintaining community structure. Often, keystone species are predators. With the loss of their predator prey populations can explode and compete with each other and strip the community of the resources needed for the survival of the prey population(s).
Question 11 |
Interactions between populations can be described as promoting the fitness of a population, having a negative impact on the fitness of a population, or having no impact on the fitness of a population. Which of the following interactions describes one in which one population benefits and the other is unaffected?
Parasitism | |
Commensalism | |
Competition | |
Mutualism |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). In a commensalism one member of the pair benefits and the other member of the pair is unaffected. For example, epiphytes are plants that grow on the upper reaches of other plants. Doing so allows the epiphyte access to sunlight. The epiphyte obtains water and nutrients from the air. The tree upon which the epiphyte grows remains unaffected.
Question 12 |
Which of the following applies to biogeography?
Humans have ear muscles which are no longer functional. | |
The Galapagos finches are all similar to one another. | |
The forelimb (arm) of a bat and that of a human have a large number of similarities. | |
The wing of a bat and the wing of a bird both play a role in flight. |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Biogeography is the study of the geographic distribution of species.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 12 questions to complete.
|
List |
